Usage v1.3.0¶
Once installed, the Quantum Origin Windows Reseed service should start automatically and start automatically every time the operating system is started. The service feeds proven quantum randomness into the Windows Entropy Pools every time the operating system’s DRBG system triggers a reseed of the Root PRNG. We call this a reseed event. The time interval between reseed events increases from startup of the operating system until stabilizing at one reseed event per hour.
Viewing Logs - Get-EventLog¶
The Windows Reseed service generates event logs every time a reseed event occurs, in order to confirm the proper operation of the service. There are two components to the Windows Reseed service: a user mode component and a kernel mode component.
During a reseed event the kernel mode component, called Quantum Origin Kernel Reseed sends proven quantum randomness to the Windows Entropy Pools. In the parlance of Windows’ DRBG system, this kernel mode component is referred to as an Entropy Source.
One can use the Get-EventLog cmdlet to get a list of event logs generated by specific source. To confirm proper operation of the kernel mode component one can run the following command
PS C:\> Get-EventLog -LogName System -Source "Quantum Origin Kernel Reseed"
and one should see some logs including the reseed event informational log

During normal operation of the Quantum Origin Windows Reseed service the user mode component, called Quantum Origin Reseed extracts proven quantum randomness from the installed instance of Quantum Origin and sends this randomness to the kernel mode service for later use in reseed events. To confirm proper operation of the user mode component one can run the following command
PS C:\> Get-EventLog -LogName Application -Source "Quantum Origin Reseed"
and one should see some logs including the randomness extraction and delivery informational log

Viewing Logs - Windows Event Viewer¶
The Windows Reseed service generates event logs every time a reseed event occurs, in order to confirm the proper operation of the service. There are two components to the Windows Reseed service: a user mode component and a kernel mode component.
During a reseed event the kernel mode component, called Quantum Origin Kernel Reseed sends proven quantum randomness to the Windows Entropy Pools. In the parlance of Windows’ DRBG system, this kernel mode component is referred to as an Entropy Source.
One can use the Windows Event Viewer to view logs generated by services and applications running on the system.
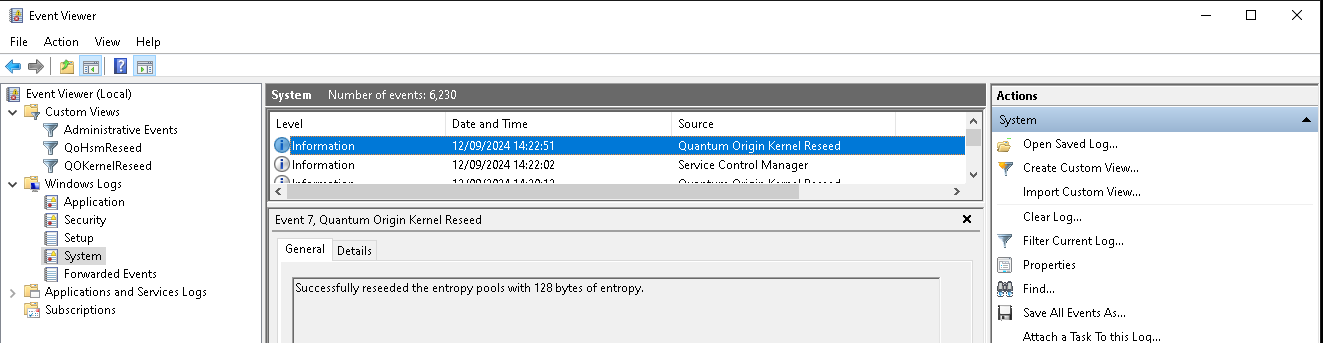
To confirm proper operation of the kernel mode component one can check the in the System panel of the Windows Event Viewer and filter for the log source Quantum Origin Kernel Reseed. Successful operation is indicated by a Successfully reseeded the entropy pools with 128 bytes of entropy log in the System Log.
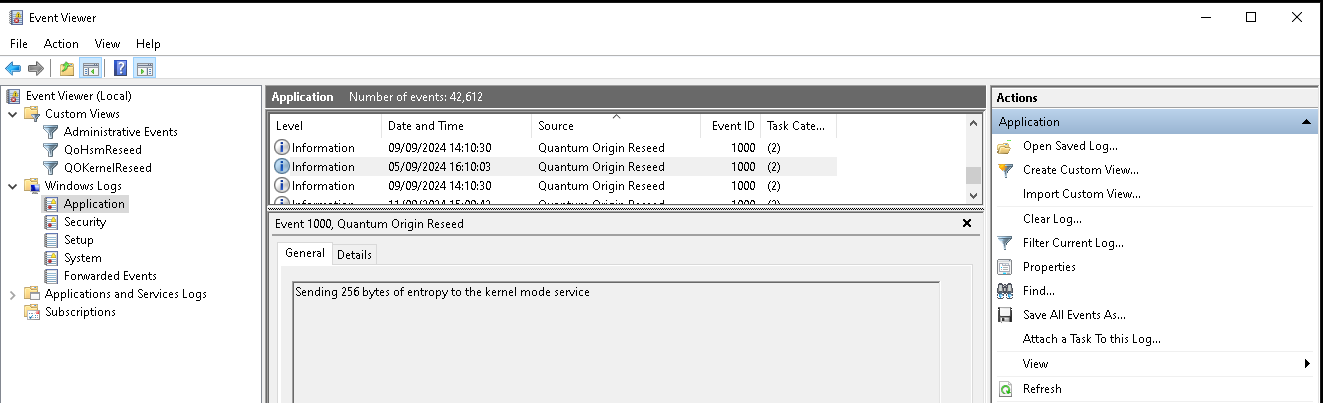
During normal operation of the Quantum Origin Windows Reseed service the user mode component, called Quantum Origin Reseed extracts proven quantum randomness from the installed instance of Quantum Origin and sends this randomness to the kernel mode service for later use in reseed events.
To confirm proper operation of the user mode component one can check the in the Application panel of the Windows Event Viewer and filter for the log source Quantum Origin Reseed.
Successful operation is determined by a Sending 256 bytes of entropy to the kernel mode service log in the Application Log.
Manual Starting and Stopping of the Service¶
When the installation of the service has been completed the service should start automatically. Once installed the service should start automatically during boot. If neither occurs, and the service is installed on the system, one can manually start the service using the Start-Service cmdlet
PS C:\> Start-Service -Name QOKernelReseed
One can then verify the service has started by using the Get-Service cmdlet and checking the status is Running
PS C:\> Get-Service -Name QOKernelReseed
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Running QOkernelreseed QOkernelreseed
If the service still does not start, please continue to Troubleshooting for further advice.
To stop the service, one can either uninstall the service or manually stop it by using either the Windows Service panel or the Stop-Service cmdlet.
PS C:\> Stop-Service -Name QOKernelReseed
WARNING: Waiting for service 'QOkernelreseed (QOkernelreseed)' to stop...
One can then verify the service has started by using the Get-Service cmdlet and checking the status is Stopped
PS C:\> Get-Service -Name QOKernelReseed
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped QOkernelreseed QOkernelreseed
If the service has not stopped, please continue to Troubleshooting for further advice.
Restarting Windows Reseed¶
Please note that in some cases the service may need to be issued a start command twice, as all handles to the driver must be closed after a stop command. These handles include the PowerShell or Services dialogue Windows, so a second start is the simplest way to resolve this. Alternatively, reboot the entire system.