Quantinuum Systems’ Workflow¶
User Authentication¶
Once a user’s email address has been set up with an account on Quantinuum Systems, an invitation email will be sent with a unique signup link to the Nexus Portal. Once registration is completed, users will need to log into the user portal to view and accept our terms and conditions before they can fully access Quantinuum systems. Usage of qnexus requires the end user to authenticate with user credentials.
Once a user’s email address has been set up with an account on Quantinuum Systems, an invitation email will be sent with a unique signup link to the Nexus Portal. To complete registration, users will need to choose how they would like to sign in: either by creating a Quantinuum account or by using third party credentials. Currently Microsoft accounts are the only third party accounts supported. Once registration is completed, users will need to log in to view and accept our terms and conditions before they can fully access Quantinuum systems. Usage of qnexus requires the end user to authenticate with user credentials.
Application Program¶
Guppy is a high-level quantum programming language embedded in python. Guppy allows Helios users to benefit from dynamical transport for programs with conditional branches. In addition, other advantages include dynamic qubit allocation (automatic qubit resource management), arbitrary real-time classical arithmetic and logic including native FOR and WHILE loops, early exit, and conditional branches with native IF (ELSE) statements. The user compiles a Guppy program to a Hierarchical Unified Group Representation (hugr), an intermediate representation. The user generates and submits hugr binaries as inputs for compile and execute jobs. Guppy is primarily designed for execution on Quantinuum Helios, but also has limited backwards compatability on System Model H2.
Pytket is a Python SDK for quantum computing. Pytket consists of a circuit builder API and also an optimizing compiler API. Pytket is primarily used to program System Model H2. Pytket can be submitted to Helios by loading the user circuit into Guppy source.
Queue¶
Compilation and Nexus-hosted execute jobs are placed in the Nexus Fair Share queue. Hardware execute jobs are routed to the fair queue. More details are available here.
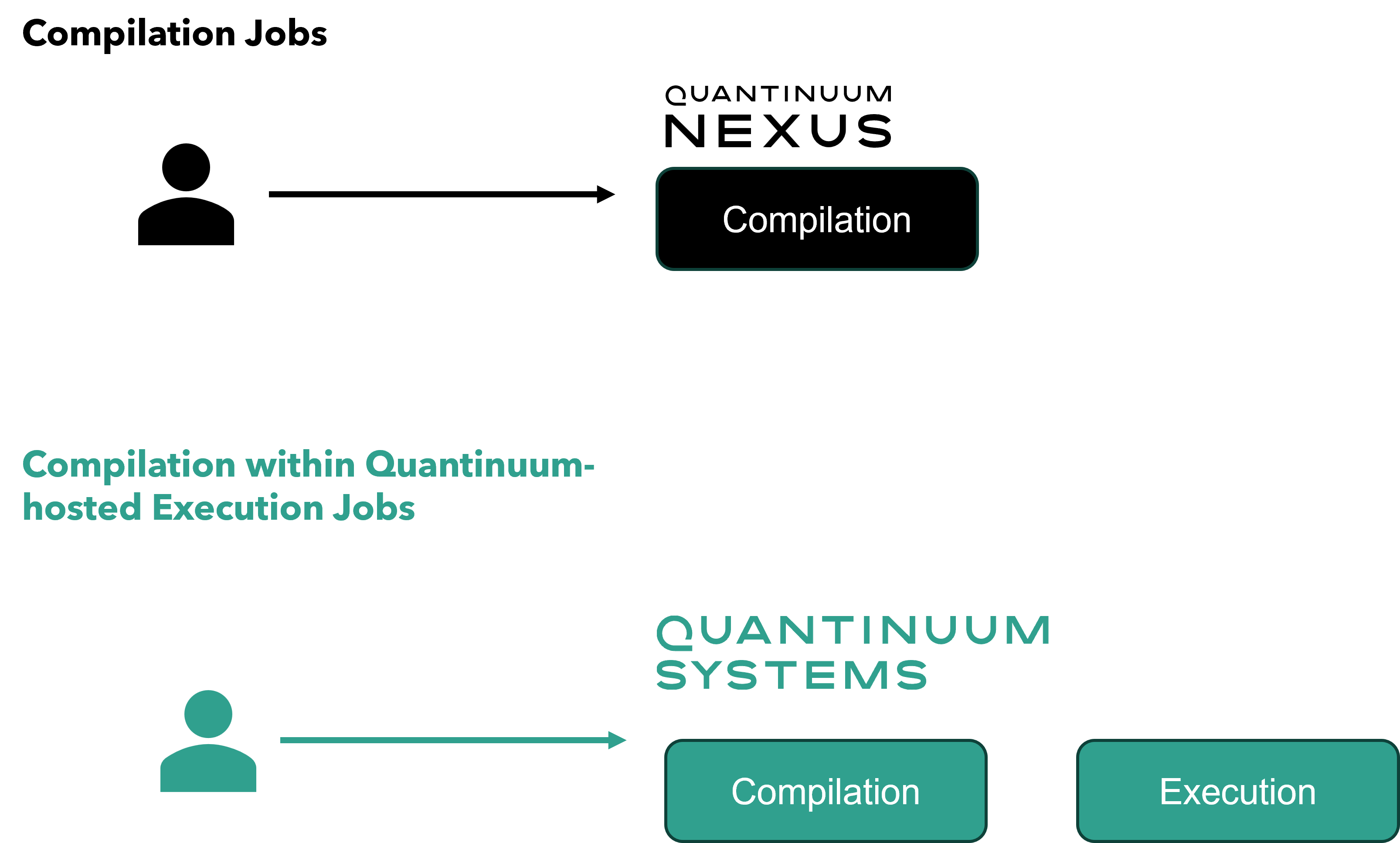
Compilation¶
Note
Nexus does not support server-side tket compilation of hugr programs.
Programs can be submitted to Nexus for server-side compilation. This enables automated translation for the quantum functions that use non-native gate operations, in addition to gate optimization. Quantum Intermediate Representation (QIR) programs are not further optimized after the execute job submission.
Job Batching¶
Quantinuum systems support the ability to run job batches. The batch feature gives users the ability to create “ad-hoc” reservations. Programs submitted together in a batch will run at one time. The benefit to users is that once a batch hits the front of the queue, jobs in a batch will run uninterrupted until they are completed.
Once a batch is submitted, jobs can continue to be added to the batch, ending either when the user signifies the end of a batch or after 1 minute of inactivity.
Batches cannot exceed the maximum batch size limit for an organization which has a default limit of 2000 HQCs. If the total HQCs for jobs in a batch hit this limit or a smaller limit set by the user, those jobs will not be cancelled. Instead, they will continue to run as regular jobs in the queue instead of as a batch.
Currently only the Quantinuum-hosted hardware and emulator targets support the batching feature. Batching is not supported on the syntax checkers.
Availability¶
The syntax checkers and emulators are nominally available 24 hours/day to subscribers via queued access. The syntax checkers are free to use while the emulators and quantum computers require HQCs.
Quantum computers are available periodically throughout a calendar month. The calendar of system availability is maintained on the Nexus portal. If needed, users can check a device’s status by first consulting the calendar on the Nexus portal. This provides day-by-day scheduling of machine availability. Calendars are frequently updated to reflect best available information.
To ensure the highest performance of Quantinuum Systems, there are periodically scheduled calibrations and upgrades on the machines. The machines are taken offline to perform the upgrades and conduct verification and validation tests to ensure consistent performance. The performance upgrades are then made available to our users. Typical improvements include upgrades to compute speed, number of available qubits, noise reduction, and overall system reliability.
Tracking Usage with Hardware Quantum Credits (HQCs)¶
All execute jobs submitted to Quantinuum Systems consume Hardware Quantum Credits (HQCs). Jobs submitted to Helios are costed differently to System Model H2 jobs. A HQC is defined as:
\(HQC = 5 + \frac{N_{1q} + 10 N_{2q} + 5 N_m}{5000} * C\),
Helios jobs benefit from conditional branching, which means overall HQC cost is dynamic to job execution. The HQC cost for a job consists of 2 parts:
a HQC cost dependent on the branches of the user’s program that are executed
an additional +5 HQC cost for a new job
Users can estimate the required HQC cost for their program by utilizing the emulator and specifying metrics as the emulation mode with the target as the Helios emulator (Helios-1E).
Run time can be reasonably predicted using the same formula that defines HQCs. Submitting to a syntax checker does not cost HQCs, but the cost of submitting the job on a quantum computer will be returned with the result for planning purposes.
where \(N_1q\) is the number of 1-qubit gates, \(N_2q\) is the number of native 2-qubit gates, \(N_m\) is the number of state preparation and measurement operations in a program, including the initial implicit state preparation and any intermediate and final measurements and resets, and \(C\) is the shot count. When a program is submitted, the cost in HQCs is returned with the results. For programs using conditional logic, the charged HQCs include all the gates and measurements across all conditional branches regardless which are executed in the program.
For hard limits on the number of HQCs per shot and per job, please see here.
Job Status¶
qnexus documentation details compile and execute job monitoring capabilities for all Quantinuum targets (link). The job status is also reported on the Nexus portal.
Data Retention¶
Data from jobs are retained in the Nexus portal indefinitely. The data retention window is consistent across all targets: quantum computers, emulators, and syntax checkers.
Upgrades¶
Quantinuum will issue Product Change Notifications (PCNs) to customers, coinciding with new upgrades. PCNs will be made commercially available, prior to any significant system changes. All PCNs are available here for customer visibility.