lambeq.backend¶
lambeq.backend.grammar¶
Grammar category¶
Lambeq’s internal representation of the grammar category. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause “New” or “Revised” License.
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Box(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, z: int = 0)[source]¶
Bases:
EntityA box in the grammar category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the box.
- domTy
The domain of the box.
- codTy
The codomain of the box.
- zint, optional
The winding number of the box, by default 0.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Cap(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxThe unit of the adjunction for an atomic type.
- Parameters:
- leftTy
The type of the left output.
- rightTy
The type of the right output.
- is_reversedbool, default: False
Whether the cap is reversed or not. Normally, caps only allow outputs where right is the left adjoint of left. However, to facilitate operations like dagger, we pass in a flag that indicates that the inputs are the opposite way round, which initialises a reversed cap. Then, when a cap is adjointed, it turns into a reversed cap, which can be adjointed again to turn it back into a normal cap.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- is_reversed: dataclasses.InitVar[bool] = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Category(name: str)[source]¶
Bases:
objectThe base class for all categories.
- __call__(name_or_entity: str) Callable[[_EntityType], _EntityType][source]¶
- __call__(name_or_entity: _EntityType) _EntityType
Call self as a function.
- __init__(name: str) None¶
- from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Entity[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into an entity from this category.
- Returns:
EntityThe entity generated from the JSON data. This could be a
Ty, aBoxsubclass, or aDiagraminstance.
- name: str¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Cup(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxThe counit of the adjunction for an atomic type.
- Parameters:
- leftTy
The type of the left output.
- rightTy
The type of the right output.
- is_reversedbool, default: False
Whether the cup is reversed or not. Normally, cups only allow inputs where right is the right adjoint of left. However, to facilitate operations like dagger, we pass in a flag that indicates that the inputs are the opposite way round, which initialises a reversed cup. Then, when a cup is adjointed, it turns into a reversed cup, which can be adjointed again to turn it back into a normal cup.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- is_reversed: dataclasses.InitVar[bool] = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Daggered(box: Box)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA daggered box.
- Parameters:
- boxBox
The box to be daggered.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram(dom: Ty, cod: Ty, layers: list[Layer])[source]¶
Bases:
EntityA diagram in the grammar category.
- Parameters:
- domTy
The type of the input wires.
- codTy
The type of the output wires.
- layerslist[Layer]
The layers of the diagram.
- classmethod caps(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod create_pregroup_diagram(words: list[Word], morphisms: list[tuple[type, int, int]]) Self[source]¶
Create a
Diagramfrom cups and swaps.>>> n, s = Ty('n'), Ty('s') >>> words = [Word('she', n), Word('goes', n.r @ s @ n.l), ... Word('home', n)] >>> morphs = [(Cup, 0, 1), (Cup, 3, 4)] >>> diagram = Diagram.create_pregroup_diagram(words, morphs)
- Parameters:
- wordslist of
Word A list of
Words corresponding to the words of the sentence.- morphisms: list of tuple[type, int, int]
- A list of tuples of the form:
(morphism, start_wire_idx, end_wire_idx).
Morphisms can be
Cups orSwaps, while the two numbers define the indices of the wires on which the morphism is applied.
- wordslist of
- Returns:
DiagramThe generated pregroup diagram.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If the provided morphism list does not type-check properly.
- classmethod cups(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- draw(draw_as_pregroup=True, **kwargs: Any) None[source]¶
Draw the diagram.
- Parameters:
- draw_as_pregroupbool, optional
Whether to try drawing the diagram as a pregroup diagram, default is True.
- draw_as_nodesbool, optional
Whether to draw boxes as nodes, default is False.
- colorstring, optional
Color of the box or node, default is white (‘#ffffff’) for boxes and red (‘#ff0000’) for nodes.
- textpadpair of floats, optional
Padding between text and wires, default is (0.1, 0.1).
- draw_type_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw type labels, default is False.
- draw_box_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw box labels, default is True.
- aspectstring, optional
Aspect ratio, one of [‘auto’, ‘equal’].
- marginstuple, optional
Margins, default is (0.05, 0.05).
- nodesizefloat, optional
BoxNode size for spiders and controlled gates.
- fontsizeint, optional
Font size for the boxes, default is 12.
- fontsize_typesint, optional
Font size for the types, default is 12.
- figsizetuple, optional
Figure size.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- to_tikzbool, optional
Whether to output tikz code instead of matplotlib.
- asymmetryfloat, optional
Make a box and its dagger mirror images, default is .25 * any(box.is_dagger for box in diagram.boxes).
- classmethod from_discopy(diagram: discopy.monoidal.Diagram) Diagram[source]¶
Import discopy diagram to lambeq diagram.
- Parameters:
- diagram
discopy.monoidal.Diagram
- diagram
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Diagram.- Returns:
DiagramThe diagram generated from the JSON data.
- property is_id: bool¶
- property is_pregroup: bool¶
Check if a diagram is a pregroup diagram.
Adapted from
discopy.grammar.pregroup.draw.- Returns:
- bool
Whether the diagram is a pregroup diagram.
- property l: Self¶
- classmethod lift(diagrams: Iterable[Diagrammable | Ty]) list[Self][source]¶
Lift diagrams to the current category.
Given a list of boxes or diagrams, call to_diagram on each, then check all of the diagrams are in the same category as the calling class.
- Parameters:
- diagramsiterable
The diagrams to lift and check.
- Returns:
- list of Diagram
The diagrams after calling to_diagram on each.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the diagrams are not in the same category of the calling class.
- normal_form(left: bool = False) Diagram[source]¶
Returns the normal form of a connected diagram, see arXiv:1804.07832.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, optional
Whether to apply left interchangers.
- Raises:
- NotImplementedError
Whenever
normalizeryields the same rewrite steps twice.
- property offsets: list[int]¶
The offset of a box is the length of the type on its left.
- classmethod permutation(dom: Ty, permutation: Iterable[int]) Self[source]¶
Create a layer of Swaps that permutes the wires.
- pregroup_normal_form()[source]¶
Applies normal form to a pregroup diagram of the form
word @ ... @ word >> wiresby normalising words and wires seperately before combining them, so it can be drawn withdraw().
- property r: Self¶
- classmethod register_special_box(name: str, diagram_factory: None = None) Callable[[_DiagrammableFactoryT], _DiagrammableFactoryT][source]¶
- classmethod register_special_box(name: str, diagram_factory: Callable[[...], Diagrammable]) None
- render_as_str(**kwargs: Any) str[source]¶
Render the diagram as text.
Presently only implemented for pregroup diagrams.
- Parameters:
- word_spacingint, default: 2
The number of spaces between the words of the diagrams.
- use_at_separatorbool, default: False
Whether to represent types using @ as the monoidal product. Otherwise, use the unicode dot character.
- compress_layersbool, default: True
Whether to draw boxes in the same layer when they can occur simultaneously, otherwise, draw one box per layer.
- use_ascii: bool, default: False
Whether to draw using ASCII characters only, for compatibility reasons.
- Returns:
- str
Drawing of diagram in string format.
- special_boxes: ClassVar[dict[str, Callable[[...], Diagrammable]]] = {'cap': <class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Cap'>, 'cup': <class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Cup'>, 'spider': <class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Spider'>, 'swap': <class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Swap'>}¶
- classmethod swap(left: Ty, right: Ty) Diagrammable[source]¶
- tensor(*diagrams: Diagrammable | Ty) Self[source]¶
- then(*diagrams: Diagrammable) Self[source]¶
- then_at(diagram: Diagrammable, index: int) Self[source]¶
- to_discopy() discopy.monoidal.Diagram[source]¶
Export lambeq diagram to discopy diagram.
- Returns:
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this diagram to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- transpose(left: bool = False) Self[source]¶
Construct the diagrammatic transpose.
The transpose of any diagram in a category with cups and caps can be constructed as follows:
(default) Left transpose Right transpose │╭╮ ╭╮│ │█│ │█│ ╰╯│ │╰╯
The input and output types of the transposed diagram are the adjoints of the respective types of the original diagram. This means that for diagrams with composite types, the order of the objects are reversed.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, default: False
Whether to transpose to the diagram to the left.
- Returns:
- Diagram
The transposed diagram, constructed as shown above.
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagrammable(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
ProtocolAn abstract base class describing the behavior of a diagram.
This is used by static type checkers that recognize structural sub-typing (duck-typing) and does not need to be explicitly subclassed.
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)¶
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
Apply a functor to the current object.
- property is_id: bool¶
Whether the current diagram is an identity diagram.
- rotate(z: int) Diagrammable[source]¶
Apply the adjoint operation z times.
If z is positive, apply the right adjoint z times. If z is negative, apply the left adjoint -z times.
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Functor(target_category: Category, ob: Callable[[Functor, Ty], Ty], ar: Callable[[Functor, Box], Diagrammable] | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
objectA functor that maps between categories.
- Parameters:
- target_categoryCategory
The category to which the functor maps.
- obcallable, optional
A function that maps types to types, by default None
- arcallable, optional
A function that maps boxes to Diagrammables, by default None
Examples
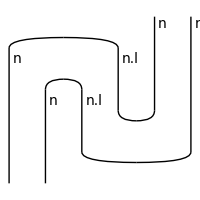
>>> n = Ty('n') >>> diag = Cap(n, n.l) @ Id(n) >> Id(n) @ Cup(n.l, n) >>> diag.draw( ... figsize=(2, 2), path='./snake.png')
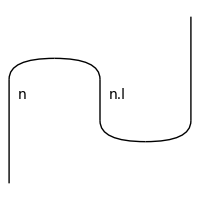
>>> F = Functor(grammar, lambda _, ty : ty @ ty) >>> F(diag).draw( ... figsize=(2, 2), path='./snake-2.png')
- __call__(entity: Ty) Ty[source]¶
- __call__(entity: Box) Diagrammable
- __call__(entity: Diagram) Diagram
- __call__(entity: Diagrammable) Diagrammable
Apply the functor to a type or a diagrammable.
- Parameters:
- entityTy or Diagrammable
The type or diagrammable to which the functor is applied.
- __init__(target_category: Category, ob: Callable[[Functor, Ty], Ty], ar: Callable[[Functor, Box], Diagrammable] | None = None) None[source]¶
- ar(ar: Box) Diagrammable[source]¶
Apply the functor to a box.
- ar_with_cache(ar: Diagrammable) Diagrammable[source]¶
Apply the functor to a diagrammable, caching the result.
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer(left: Ty, box: Box, right: Ty)[source]¶
Bases:
EntityA layer in a diagram.
- Parameters:
- boxBox
The box in the layer.
- leftTy
The wire type to the left of the box.
- rightTy
The wire type to the right of the box.
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Layer.- Returns:
LayerThe layer generated from the JSON data.
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this layer to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Spider(type: Ty, n_legs_in: int, n_legs_out: int)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA spider in the grammar category.
- Parameters:
- typeTy
The atomic type of the spider.
- n_legs_inint
The number of input legs.
- n_legs_outint
The number of output legs.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- n_legs_in: int¶
- n_legs_out: int¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Swap(left: Ty, right: Ty)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA swap in the grammar category.
Swaps two wires.
- Parameters:
- leftTy
The atomic type of the left input wire.
- rightTy
The atomic type of the right input wire.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty(name: str | None = None, objects: list[~typing.Self] = <factory>, z: int = 0)[source]¶
Bases:
EntityA type in the grammar category.
Every type is either atomic, complex, or empty. Complex types are tensor products of atomic types, and empty types are the identity type.
- Parameters:
- namestr, optional
The name of the type, by default None.
- objectslist[Ty], optional
The objects defining a complex type, by default [].
- zint, optional
The winding number of the type, by default 0.
- __init__(name: str | None = None, objects: list[~typing.Self] = <factory>, z: int = 0) None¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Ty.- Returns:
TyThe type generated from the JSON data.
- property is_atomic: bool¶
- property is_complex: bool¶
- property is_empty: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- name: str | None = None¶
- objects: list[Self]¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this type to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.grammar.Word(name: str, cod: Ty, z: int = 0)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA word in the grammar category.
A word is a
Boxwith an empty domain.- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the word.
- codTy
The codomain of the word.
- zint, optional
The winding number of the word, by default 0
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='grammar', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
lambeq.backend.tensor¶
Tensor category¶
Lambeq’s internal representation of the tensor category. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause ‘New’ or ‘Revised’ License.
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Box(name: str, dom: Dim, cod: Dim, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxBox (tensor) in the the tensor category.
- Attributes:
- datanp.array or float or None
Data used to represent the array attribute. Typically either the array itself, or a symbolic array.
- arraynp.array or float
Tensor which the box represents.
- free_symbolsset of sympy.Symbol
In case of a symbolic tensor, set of symbols in the box’s data.
- __init__(name: str, dom: Dim, cod: Dim, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0)[source]¶
Initialise a tensor.Box type.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name for the box.
- domDim
Dimension of the box’s domain.
- codDim
Dimension of the box’s codomain.
- datafloat or np.ndarray, optional
The concrete tensor the box represents.
- zint, optional
Winding number of the box, indicating conjugation. Starts at 0 if not provided.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable[source]¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)[source]¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Cap(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
-
A Cap in the tensor category.
- __init__(left: Dim, right: Dim, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
Initialise a tensor Cap.
- Parameters:
- leftDim
Dimension (type) of the left leg of the cap. Must be the conjugate of right.
- rightDim
Dimension (type) of the right leg of the cap. Must be the conjugate of left.
- is_reversedbool, default False
Ignored parameter, since left and right conjugates are equivalent in the tensor category. Necessary to inherit from grammar.Cap appropriately.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- is_reversed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Cup(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
-
A Cup in the tensor category.
- __init__(left: Dim, right: Dim, is_reversed: bool = False)[source]¶
Initialise a tensor Cup.
- Parameters:
- leftDim
Dimension (type) of the left leg of the cup. Must be the conjugate of right.
- rightDim
Dimension (type) of the right leg of the cup. Must be the conjugate of left.
- is_reversedbool, default False
Ignored parameter, since left and right conjugates are equivalent in the tensor category. Necessary to inherit from grammar.Cup appropriately.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- is_reversed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Daggered(box: Box)[source]¶
-
A daggered box.
- Attributes:
- boxBox
The box to be daggered.
- __init__(box: Box) None¶
Initialise a tensor.Box type.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name for the box.
- domDim
Dimension of the box’s domain.
- codDim
Dimension of the box’s codomain.
- datafloat or np.ndarray, optional
The concrete tensor the box represents.
- zint, optional
Winding number of the box, indicating conjugation. Starts at 0 if not provided.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None = None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram(dom: Dim, cod: Dim, layers: list[Layer])[source]¶
Bases:
DiagramDiagram in the tensor category.
- classmethod caps(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod create_pregroup_diagram(words: list[Word], morphisms: list[tuple[type, int, int]]) Self[source]¶
Create a
Diagramfrom cups and swaps.>>> n, s = Ty('n'), Ty('s') >>> words = [Word('she', n), Word('goes', n.r @ s @ n.l), ... Word('home', n)] >>> morphs = [(Cup, 0, 1), (Cup, 3, 4)] >>> diagram = Diagram.create_pregroup_diagram(words, morphs)
- Parameters:
- wordslist of
Word A list of
Words corresponding to the words of the sentence.- morphisms: list of tuple[type, int, int]
- A list of tuples of the form:
(morphism, start_wire_idx, end_wire_idx).
Morphisms can be
Cups orSwaps, while the two numbers define the indices of the wires on which the morphism is applied.
- wordslist of
- Returns:
DiagramThe generated pregroup diagram.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If the provided morphism list does not type-check properly.
- classmethod cups(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- draw(draw_as_pregroup=True, **kwargs: Any) None[source]¶
Draw the diagram.
- Parameters:
- draw_as_pregroupbool, optional
Whether to try drawing the diagram as a pregroup diagram, default is True.
- draw_as_nodesbool, optional
Whether to draw boxes as nodes, default is False.
- colorstring, optional
Color of the box or node, default is white (‘#ffffff’) for boxes and red (‘#ff0000’) for nodes.
- textpadpair of floats, optional
Padding between text and wires, default is (0.1, 0.1).
- draw_type_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw type labels, default is False.
- draw_box_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw box labels, default is True.
- aspectstring, optional
Aspect ratio, one of [‘auto’, ‘equal’].
- marginstuple, optional
Margins, default is (0.05, 0.05).
- nodesizefloat, optional
BoxNode size for spiders and controlled gates.
- fontsizeint, optional
Font size for the boxes, default is 12.
- fontsize_typesint, optional
Font size for the types, default is 12.
- figsizetuple, optional
Figure size.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- to_tikzbool, optional
Whether to output tikz code instead of matplotlib.
- asymmetryfloat, optional
Make a box and its dagger mirror images, default is .25 * any(box.is_dagger for box in diagram.boxes).
- eval(contractor=<function auto>, dtype: type | None = None)[source]¶
Evaluate the tensor diagram.
- Parameters:
- contractortn contractor
tensornetwork contractor for chosen contraction algorithm.
- dtypetype, optional
Data type of the resulting array. Defaults to np.float32.
- Returns:
- numpy.ndarray
n-dimension array representing the contracted tensor.
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_discopy(diagram: discopy.monoidal.Diagram) Diagram[source]¶
Import discopy diagram to lambeq diagram.
- Parameters:
- diagram
discopy.monoidal.Diagram
- diagram
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Diagram.- Returns:
DiagramThe diagram generated from the JSON data.
- property is_id: bool¶
- property is_pregroup: bool¶
Check if a diagram is a pregroup diagram.
Adapted from
discopy.grammar.pregroup.draw.- Returns:
- bool
Whether the diagram is a pregroup diagram.
- property l: Self¶
- classmethod lift(diagrams: Iterable[Diagrammable | Ty]) list[Self][source]¶
Lift diagrams to the current category.
Given a list of boxes or diagrams, call to_diagram on each, then check all of the diagrams are in the same category as the calling class.
- Parameters:
- diagramsiterable
The diagrams to lift and check.
- Returns:
- list of Diagram
The diagrams after calling to_diagram on each.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the diagrams are not in the same category of the calling class.
- normal_form(left: bool = False) Diagram[source]¶
Returns the normal form of a connected diagram, see arXiv:1804.07832.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, optional
Whether to apply left interchangers.
- Raises:
- NotImplementedError
Whenever
normalizeryields the same rewrite steps twice.
- property offsets: list[int]¶
The offset of a box is the length of the type on its left.
- classmethod permutation(dom: Ty, permutation: Iterable[int]) Self[source]¶
Create a layer of Swaps that permutes the wires.
- pregroup_normal_form()[source]¶
Applies normal form to a pregroup diagram of the form
word @ ... @ word >> wiresby normalising words and wires seperately before combining them, so it can be drawn withdraw().
- property r: Self¶
- classmethod register_special_box(name: str, diagram_factory: Callable[[...], Diagrammable] | None = None) None | Callable[[_DiagrammableFactoryT], _DiagrammableFactoryT][source]¶
- render_as_str(**kwargs: Any) str[source]¶
Render the diagram as text.
Presently only implemented for pregroup diagrams.
- Parameters:
- word_spacingint, default: 2
The number of spaces between the words of the diagrams.
- use_at_separatorbool, default: False
Whether to represent types using @ as the monoidal product. Otherwise, use the unicode dot character.
- compress_layersbool, default: True
Whether to draw boxes in the same layer when they can occur simultaneously, otherwise, draw one box per layer.
- use_ascii: bool, default: False
Whether to draw using ASCII characters only, for compatibility reasons.
- Returns:
- str
Drawing of diagram in string format.
- special_boxes: ClassVar[dict[str, _DiagrammableFactory]] = {'cap': <class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Cap'>, 'cup': <class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Cup'>, 'spider': <class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Spider'>, 'swap': <class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Swap'>}¶
- classmethod swap(left: Ty, right: Ty) Diagrammable[source]¶
- tensor(*diagrams: Diagrammable | Ty) Self[source]¶
- then(*diagrams: Diagrammable) Self[source]¶
- then_at(diagram: Diagrammable, index: int) Self[source]¶
- to_discopy() discopy.monoidal.Diagram[source]¶
Export lambeq diagram to discopy diagram.
- Returns:
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this diagram to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- to_tn(dtype: type | None = None)[source]¶
Convert the diagram to a tensornetwork TN.
- Parameters:
- dtypetype, optional
Data type of the resulting array. Defaults to np.float32.
- Returns:
- tuple[list[tn.Node], list[tn.Edge]]
tensornetwork representation of the diagram. An edge object is returned for each dangling edge in the network.
- transpose(left: bool = False) Self[source]¶
Construct the diagrammatic transpose.
The transpose of any diagram in a category with cups and caps can be constructed as follows:
(default) Left transpose Right transpose │╭╮ ╭╮│ │█│ │█│ ╰╯│ │╰╯
The input and output types of the transposed diagram are the adjoints of the respective types of the original diagram. This means that for diagrams with composite types, the order of the objects are reversed.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, default: False
Whether to transpose to the diagram to the left.
- Returns:
- Diagram
The transposed diagram, constructed as shown above.
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim(*dim: int, objects: list[Self] | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
TyDimension in the tensor category.
- Attributes:
- dimtuple of int
Tuple of dimensions represented by the object.
- product: int
Product of contained dimensions.
- __init__(*dim: int, objects: list[Self] | None = None) None[source]¶
Initialise a Dim type.
- Parameters:
- dimlist[int]
List of dimensions to initialise.
- objects: list[Self] or None, default None
List of Dim`s, to prepare a non-atomic `Dim object.
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- count(other: Self) int¶
- property dim: tuple[int, ...]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Ty.- Returns:
TyThe type generated from the JSON data.
- property is_atomic: bool¶
- property is_complex: bool¶
- property is_empty: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- name: str | None = None¶
- objects: list[Self]¶
- property product: int¶
- property r: Self¶
- repeat(times: int) Self¶
- tensor(other: Self | Iterable[Self], *rest: Self) Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this type to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer(left: Dim, box: Box, right: Dim)[source]¶
Bases:
LayerLayer in the tensor category.
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Layer.- Returns:
LayerThe layer generated from the JSON data.
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this layer to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Spider(type: Ty, n_legs_in: int, n_legs_out: int)[source]¶
-
A Spider in the tensor category.
Concretely represented by a copy node.
- __init__(type: Dim, n_legs_in: int, n_legs_out: int)[source]¶
Initialise a tensor Spider.
- Parameters:
- typeDim
Dimension (type) of each leg of the spider.
- n_legs_inint
Number of input legs of the spider.
- n_legs_outint
Number of input legs of the spider.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- n_legs_in: int¶
- n_legs_out: int¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.tensor.Swap(left: Ty, right: Ty)[source]¶
-
A Swap in the tensor category.
- __init__(left: Dim, right: Dim)[source]¶
Initialise a tensor Swap.
- Parameters:
- leftDim
Dimension (type) of the left input of the swap.
- rightDim
Dimension (type) of the right input of the swap.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='tensor', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Dim'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
lambeq.backend.quantum¶
Quantum category¶
Lambeq’s internal representation of the quantum category. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause ‘New’ or ‘Revised’ License.
Notes¶
In lambeq, gates are represented as the transpose of their matrix according to the standard convention in quantum computing. This makes composition of gates using the tensornetwork library easier.
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.AntiConjugate(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxAn anti-conjugate box is equal to the conjugate of its conjugate.
- __init__(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)[source]¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Bit(*bitstring: int)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxClassical state for a given bit.
- __init__(bit_value: int) None[source]¶
Initialise a ket box.
- Parameters:
- bit_valueint
The state of the qubit (either 0 or 1).
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Box(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA box in the quantum category.
- __init__(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable[source]¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)[source]¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Bra(*bitstring: int)[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugate,BoxA bra in the quantum category.
A bra is a box that measures a qubit in the computational basis and post-selects on a given state.
- __init__(bit: int)[source]¶
Initialise a bra box.
- Parameters:
- bitint
The state of the qubit to post-select on (either 0 or 1).
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- lambeq.backend.quantum.CRx(phi, distance=1)¶
- lambeq.backend.quantum.CRy(phi, distance=1)¶
- lambeq.backend.quantum.CRz(phi, distance=1)¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Controlled(controlled: Box, distance=1)[source]¶
Bases:
ParametrizedA gate that applies a unitary controlled by a qubit’s state.
- __init__(controlled: Box, distance=1)[source]¶
Initialise a controlled box.
- Parameters:
- controlledBox
The box to be controlled.
- distanceint, optional
The distance between the control and the target, by default 1
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property phase: float¶
- property r: Self¶
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Daggered(box: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], int] = <function Box.__hash__>, __repr__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], str] = <function Box.__repr__>)[source]¶
-
A daggered gate reverses the box’s effect on a quantum state.
- Parameters:
- boxBox
The box to be daggered.
- __init__(box: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], int] = <function Box.__hash__>, __repr__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], str] = <function Box.__repr__>) None¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None = None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram(dom: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty, cod: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty, layers: list[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer], __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[], int] = <function Diagram.__hash__>)[source]¶
Bases:
DiagramA diagram in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- domTy
The type of the input wires.
- codTy
The type of the output wires.
- layerslist[Layer]
The layers of the diagram.
- __init__(dom: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty, cod: ~lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty, layers: list[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer], __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[], int] = <function Diagram.__hash__>) None¶
- apply_parametrized_gate(gate: Callable[[float], Parametrized], param: float, *qubits: int) Self[source]¶
- classmethod caps(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod create_pregroup_diagram(words: list[Word], morphisms: list[tuple[type, int, int]]) Self[source]¶
Create a
Diagramfrom cups and swaps.>>> n, s = Ty('n'), Ty('s') >>> words = [Word('she', n), Word('goes', n.r @ s @ n.l), ... Word('home', n)] >>> morphs = [(Cup, 0, 1), (Cup, 3, 4)] >>> diagram = Diagram.create_pregroup_diagram(words, morphs)
- Parameters:
- wordslist of
Word A list of
Words corresponding to the words of the sentence.- morphisms: list of tuple[type, int, int]
- A list of tuples of the form:
(morphism, start_wire_idx, end_wire_idx).
Morphisms can be
Cups orSwaps, while the two numbers define the indices of the wires on which the morphism is applied.
- wordslist of
- Returns:
DiagramThe generated pregroup diagram.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If the provided morphism list does not type-check properly.
- classmethod cups(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagrammable[source]¶
- draw(draw_as_pregroup=True, **kwargs: Any) None[source]¶
Draw the diagram.
- Parameters:
- draw_as_pregroupbool, optional
Whether to try drawing the diagram as a pregroup diagram, default is True.
- draw_as_nodesbool, optional
Whether to draw boxes as nodes, default is False.
- colorstring, optional
Color of the box or node, default is white (‘#ffffff’) for boxes and red (‘#ff0000’) for nodes.
- textpadpair of floats, optional
Padding between text and wires, default is (0.1, 0.1).
- draw_type_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw type labels, default is False.
- draw_box_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw box labels, default is True.
- aspectstring, optional
Aspect ratio, one of [‘auto’, ‘equal’].
- marginstuple, optional
Margins, default is (0.05, 0.05).
- nodesizefloat, optional
BoxNode size for spiders and controlled gates.
- fontsizeint, optional
Font size for the boxes, default is 12.
- fontsize_typesint, optional
Font size for the types, default is 12.
- figsizetuple, optional
Figure size.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- to_tikzbool, optional
Whether to output tikz code instead of matplotlib.
- asymmetryfloat, optional
Make a box and its dagger mirror images, default is .25 * any(box.is_dagger for box in diagram.boxes).
- eval(*others, backend=None, mixed=False, contractor=<function auto>, **params)[source]¶
Evaluate the circuit represented by the diagram.
Be aware that this method is only suitable for small circuits with a small number of qubits (depending on hardware resources).
- Parameters:
- others
lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram Other circuits to process in batch if backend is set to tket.
- backendpytket.Backend, optional
Backend on which to run the circuit, if none then we apply tensor contraction.
- mixedbool, optional
Whether the circuit is mixed, by default False
- contractorCallable, optional
The contractor to use, by default tn.contractors.auto
- others
- Returns:
- np.ndarray or list of np.ndarray
The result of the circuit simulation.
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_discopy(diagram: discopy.monoidal.Diagram) Diagram[source]¶
Import discopy diagram to lambeq diagram.
- Parameters:
- diagram
discopy.monoidal.Diagram
- diagram
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Diagram.- Returns:
DiagramThe diagram generated from the JSON data.
- property is_id: bool¶
- property is_mixed: bool¶
Whether the diagram is mixed.
A diagram is mixed if it contains a mixed box or if it has both classical and quantum wires.
- property is_pregroup: bool¶
Check if a diagram is a pregroup diagram.
Adapted from
discopy.grammar.pregroup.draw.- Returns:
- bool
Whether the diagram is a pregroup diagram.
- property l: Self¶
- classmethod lift(diagrams: Iterable[Diagrammable | Ty]) list[Self][source]¶
Lift diagrams to the current category.
Given a list of boxes or diagrams, call to_diagram on each, then check all of the diagrams are in the same category as the calling class.
- Parameters:
- diagramsiterable
The diagrams to lift and check.
- Returns:
- list of Diagram
The diagrams after calling to_diagram on each.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If any of the diagrams are not in the same category of the calling class.
- normal_form(left: bool = False) Diagram[source]¶
Returns the normal form of a connected diagram, see arXiv:1804.07832.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, optional
Whether to apply left interchangers.
- Raises:
- NotImplementedError
Whenever
normalizeryields the same rewrite steps twice.
- property offsets: list[int]¶
The offset of a box is the length of the type on its left.
- classmethod permutation(dom: Ty, permutation: Iterable[int]) Self[source]¶
Create a layer of Swaps that permutes the wires.
- pregroup_normal_form()[source]¶
Applies normal form to a pregroup diagram of the form
word @ ... @ word >> wiresby normalising words and wires seperately before combining them, so it can be drawn withdraw().
- property r: Self¶
- classmethod register_special_box(name: str, diagram_factory: Callable[[...], Diagrammable] | None = None) None | Callable[[_DiagrammableFactoryT], _DiagrammableFactoryT][source]¶
- render_as_str(**kwargs: Any) str[source]¶
Render the diagram as text.
Presently only implemented for pregroup diagrams.
- Parameters:
- word_spacingint, default: 2
The number of spaces between the words of the diagrams.
- use_at_separatorbool, default: False
Whether to represent types using @ as the monoidal product. Otherwise, use the unicode dot character.
- compress_layersbool, default: True
Whether to draw boxes in the same layer when they can occur simultaneously, otherwise, draw one box per layer.
- use_ascii: bool, default: False
Whether to draw using ASCII characters only, for compatibility reasons.
- Returns:
- str
Drawing of diagram in string format.
- special_boxes: ClassVar[dict[str, _DiagrammableFactory]] = {'cap': <function generate_cap>, 'cup': <function generate_cup>, 'spider': <function generate_spider>, 'swap': <class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Swap'>}¶
- classmethod swap(left: Ty, right: Ty) Diagrammable[source]¶
- tensor(*diagrams: Diagrammable | Ty) Self[source]¶
- then(*diagrams: Diagrammable) Self[source]¶
- then_at(diagram: Diagrammable, index: int) Self[source]¶
- to_discopy() discopy.monoidal.Diagram[source]¶
Export lambeq diagram to discopy diagram.
- Returns:
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this diagram to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- to_pennylane(probabilities=False, backend_config=None, diff_method='best')[source]¶
Export lambeq circuit to PennylaneCircuit.
- Parameters:
- probabiltiesbool, default: False
If True, the PennylaneCircuit will return the normalized probabilties of measuring the computational basis states when run. If False, it returns the unnormalized quantum states in the computational basis.
- backend_configdict, default: None
A dictionary of PennyLane backend configration options, including the provider (e.g. IBM or Honeywell), the device, the number of shots, etc. See the PennyLane plugin documentation for more details.
- diff_methodstr, default: “best”
The differentiation method to use to obtain gradients for the PennyLane circuit. Some gradient methods are only compatible with simulated circuits. See the PennyLane documentation for more details.
- Returns:
lambeq.backend.pennylane.PennylaneCircuit
- to_tk()[source]¶
Export to t|ket>.
- Returns:
- tk_circuitlambeq.backend.converters.tk.Circuit
Examples
>>> from lambeq.backend.quantum import *
>>> bell_test = H @ Id(qubit) >> CX >> Measure() @ Measure() >>> bell_test.to_tk() tk.Circuit(2, 2).H(0).CX(0, 1).Measure(0, 0).Measure(1, 1)
>>> circuit0 = (Sqrt(2) @ H @ Rx(0.5) >> CX >> ... Measure() @ Discard()) >>> circuit0.to_tk() tk.Circuit(2, 1).H(0).Rx(1.0, 1).CX(0, 1).Measure(0, 0).scale(2)
>>> circuit1 = Ket(1, 0) >> CX >> Id(qubit) @ Ket(0) @ Id(qubit) >>> circuit1.to_tk() tk.Circuit(3).X(0).CX(0, 2)
>>> circuit2 = X @ Id(qubit ** 2) \ ... >> Id(qubit) @ SWAP >> CX @ Id(qubit) >> Id(qubit) @ SWAP >>> circuit2.to_tk() tk.Circuit(3).X(0).CX(0, 2)
>>> circuit3 = Ket(0, 0)\ ... >> H @ Id(qubit)\ ... >> CX\ ... >> Id(qubit) @ Bra(0) >>> print(repr(circuit3.to_tk())) tk.Circuit(2, 1).H(0).CX(0, 1).Measure(1, 0).post_select({0: 0})
- to_tn(mixed=False)[source]¶
Send a diagram to a mixed
tensornetwork.- Parameters:
- mixedbool, default: False
Whether to perform mixed (also known as density matrix) evaluation of the circuit.
- Returns:
- nodes
tensornetwork.Node Nodes of the network.
- output_edge_orderlist of
tensornetwork.Edge Output edges of the network.
- nodes
- transpose(left: bool = False) Self[source]¶
Construct the diagrammatic transpose.
The transpose of any diagram in a category with cups and caps can be constructed as follows:
(default) Left transpose Right transpose │╭╮ ╭╮│ │█│ │█│ ╰╯│ │╰╯
The input and output types of the transposed diagram are the adjoints of the respective types of the original diagram. This means that for diagrams with composite types, the order of the objects are reversed.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, default: False
Whether to transpose to the diagram to the left.
- Returns:
- Diagram
The transposed diagram, constructed as shown above.
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Discard[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugateDiscard a qubit. This is a measurement without post-selection.
- __init__()[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Encode[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugateEncode a classical information bit into a qubit.
- __init__()[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Ket(*bitstring: int)[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugate,BoxA ket in the quantum category.
A ket is a box that initializes a qubit to a given state.
- __init__(bit: int) None[source]¶
Initialise a ket box.
- Parameters:
- bitint
The state of the qubit (either 0 or 1).
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer(left: Ty, box: Box, right: Ty)[source]¶
Bases:
LayerA Layer in a quantum Diagram.
- Parameters:
- boxBox
The box of the layer.
- leftTy
The wire type to the left of the box.
- rightTy
The wire type to the right of the box.
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Layer.- Returns:
LayerThe layer generated from the JSON data.
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this layer to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Measure[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugateMeasure a qubit and return a classical information bit.
- __init__()[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.MixedState[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugateA mixed state is a state with a density matrix proportional to the identity matrix.
- __init__()[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Parametrized(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA parametrized box in the quantum category.
A parametrized box is a unitary gate that can be parametrized by a real number.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the box.
- domTy
The domain of the box.
- codTy
The codomain of the box.
- datafloat
The parameterised unitary of the box.
- is_mixedbool, default: False
Whether the box is mixed
- self_adjointbool, default: False
Whether the box is self-adjoint
- __init__(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Rotation(phase)[source]¶
Bases:
ParametrizedSingle qubit gate defining a rotation around the bloch sphere.
- __init__(phase)[source]¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols, **kwargs)¶
Return a lambda function that evaluates the box.
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property phase: float¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Rx(phase)[source]¶
Bases:
AntiConjugate,RotationSingle qubit gate defining a rotation aound the x-axis.
- __init__(phase)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- dagger() Self¶
Return the dagger of the box.
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols, **kwargs)¶
Return a lambda function that evaluates the box.
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property phase: float¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Ry(phase)[source]¶
Bases:
SelfConjugate,RotationSingle qubit gate defining a rotation aound the y-axis.
- __init__(phase)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- dagger() Self¶
Return the dagger of the box.
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols, **kwargs)¶
Return a lambda function that evaluates the box.
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property phase: float¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Rz(phase)[source]¶
Bases:
AntiConjugate,RotationSingle qubit gate defining a rotation aound the z-axis.
- __init__(phase)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- dagger() Self¶
Return the dagger of the box.
- data: float¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols, **kwargs)¶
Return a lambda function that evaluates the box.
- property modules¶
- name: str¶
- property phase: float¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Scalar(data: float | ~numpy.ndarray, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], int] = <function Box.__hash__>)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA scalar amplifies a quantum state by a given factor.
- __init__(data: float | ~numpy.ndarray, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[~lambeq.backend.quantum.Box], int] = <function Box.__hash__>) None¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.SelfConjugate(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)[source]¶
Bases:
BoxA self-conjugate box is equal to its own conjugate.
- __init__(name: str, dom: Ty, cod: Ty, data: float | ndarray | None = None, z: int = 0, is_mixed: bool = False, self_adjoint: bool = False)¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z)[source]¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Sqrt(data: float | ~numpy.ndarray, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[], int] = <function Box.__hash__>)[source]¶
Bases:
ScalarA Square root.
- __init__(data: float | ~numpy.ndarray, __hash__: ~collections.abc.Callable[[], int] = <function Box.__hash__>) None¶
Initialise a box in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr
Name of the box.
- domTy
Domain of the box.
- codTy
Codomain of the box.
- datafloat | np.ndarray, optional
Array defining the tensor of the box, by default None
- zint, optional
The winding number, by default 0
- is_mixedbool, optional
Whether the box is mixed, by default False
- self_adjointbool, optional
Whether the box is self-adjoint, by default False
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool = False¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int)¶
Get the result of conjugating the box z times.
- Parameters:
- zint
Winding count. The number of conjugations to apply to the box.
- Returns:
- Box
The box conjugated z times.
- self_adjoint: bool = False¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Swap(left: Ty, right: Ty)[source]¶
Bases:
Swap,SelfConjugate,BoxA swap box in the quantum category.
- __init__(left: Ty, right: Ty)[source]¶
Initialise a swap box.
- Parameters:
- leftTy
The left type of the swap.
- rightTy
The right type of the swap.
- apply_functor(functor: Functor) Diagrammable[source]¶
- property array¶
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- data: float | np.ndarray | None¶
- property free_symbols: set[Symbol]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Box.- Returns:
BoxThe box generated from the JSON data.
- property is_classical: bool¶
- is_mixed: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- lambdify(*symbols: Symbol, **kwargs) Callable¶
Get a lambdified version of a symbolic box.
Returns a function which when provided appropriate parameters, initialises a concrete box.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of sympy.Symbols
List of symbols in the box in the order in which their assigned values will appear in the concretisation call.
- kwargs:
Additional parameters to pass to sympy.lambdify.
- Returns:
- Callable[…, Box]:
A lambda function which when invoked with appropriate parameters, returns a concrete version of the box.
- n_legs_in: int¶
- n_legs_out: int¶
- name: str¶
- property r: Self¶
- self_adjoint: bool¶
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this box to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- unwind() Self¶
- z: int = 0¶
- class lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty(name: str | None = None, objects: list[Self] | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
DimA type in the quantum category.
- __init__(name: str | None = None, objects: list[Self] | None = None)[source]¶
Initialise a type in the quantum category.
- Parameters:
- namestr, optional
The name of the type, by default None
- objectslist[Ty], optional
The objects defining a complex type, by default None
- category: ClassVar[Category] = Category(name='quantum', Ty=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Ty'>, Box=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Box'>, Layer=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Layer'>, Diagram=<class 'lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram'>)¶
- property dim: tuple[int, ...]¶
- classmethod from_json(data: Dict[str, Any] | str) Self[source]¶
Decode a JSON object or string into a
Ty.- Returns:
TyThe type generated from the JSON data.
- property is_atomic: bool¶
- property is_complex: bool¶
- property is_empty: bool¶
- property l: Self¶
- name: str | None = None¶
- objects: list[Self]¶
- property product: int¶
- property r: Self¶
- rotate(z: int) Self¶
Rotate the type, changing the winding number.
- to_json(is_top_level: bool = True) Dict[str, Any][source]¶
Encode this type to a JSON object.
- Parameters:
- is_top_levelbool, optional
This flag indicates that this object is the top-most object and should have the global metadata (e.g. category). This should be set to False when calling to_json on attribute instances to avoid duplication of said global metadata.
- z: int = 0¶
- lambeq.backend.quantum.generate_cap(left: Ty, right: Ty, is_reversed=False) Diagram[source]¶
Generate a cap diagram.
- Parameters:
- leftTy
The left type of the cap.
- rightTy
The right type of the cap.
- is_reversedbool, optional
Unused, by default False
- Returns:
- Diagram
The cap diagram.
lambeq.backend.numerical_backend¶
Numerical Backend¶
Module unifying the use of numerical backends for lambeq. This module is used to provide a common interface to different numerical backends, such as NumPy, JAX, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
- class lambeq.backend.numerical_backend.Backend(module: ModuleType, array: Callable | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
objectA matrix backend.
- Parameters:
module : The main module of the backend. array : The array class of the backend.
- property name¶
- class lambeq.backend.numerical_backend.PyTorch[source]¶
Bases:
BackendPyTorch backend.
- property name¶
- class lambeq.backend.numerical_backend.TensorFlow[source]¶
Bases:
BackendTensorFlow backend.
- property name¶
lambeq.backend.converters.discopy¶
Interface with discopy¶
Module containing the functions to convert from and to discopy. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause “New” or “Revised” License.
- lambeq.backend.converters.discopy.box_d2l(box: Box, target: type[_LAMBEQ_BOX_VAR]) _LAMBEQ_BOX_VAR[source]¶
- lambeq.backend.converters.discopy.box_l2d(box: Box, target: type[_DISCOPY_BOX_VAR]) _DISCOPY_BOX_VAR[source]¶
- lambeq.backend.converters.discopy.from_discopy(diagram: Diagram | Circuit | Diagram) Diagram | Diagram | Diagram[source]¶
Takes a
discopy.grammar.pregroup.Diagram,discopy.quantum.Diagram, ordiscopy.tensor.Diagram, and converts it to alambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram,lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram, orlambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram, respectively.- Parameters:
- diagram
discopy.grammar.pregroup.Diagram| discopy.quantum.Diagram|discopy.tensor.DiagramThe diagram to convert.
- diagram
- Returns:
lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram|lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram|lambeq.backend.tensor.DiagramThe converted diagram.
- lambeq.backend.converters.discopy.to_discopy(diagram: Diagram | Diagram | Diagram) Diagram | Circuit | Diagram[source]¶
Takes a
lambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram,lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram, orlambeq.backend.tensor.Diagram, and converts it to adiscopy.grammar.pregroup.Diagram,discopy.quantum.Diagram, ordiscopy.tensor.Diagram, respectively.- Parameters:
- diagramlambeq.backend.grammar.Diagram |
lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram|lambeq.backend.tensor.DiagramThe diagram to convert.
- Returns:
- :class:
discopy.grammar.pregroup.Diagram| discopy.quantum.Diagram|discopy.tensor.DiagramThe converted diagram.
- :class:
lambeq.backend.converters.tk¶
Interface with tket¶
Module containing the functions to convert from and to tket. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause “New” or “Revised” License.
- class lambeq.backend.converters.tk.Circuit(n_qubits: int = 0, n_bits: int = 0, post_selection: dict[int, int] | None = None, scalar: float | None = None, post_processing: Diagram | None = None)[source]¶
Bases:
CircuitExtend pytket.Circuit with counts post-processing.
- AAMS(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
AAMS(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an AAMS gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
AAMS(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an AAMS gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CCX(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CCX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_0: int, control_1: int, target: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CCX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CCX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, control_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CCX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CH(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CH(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CH gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CH(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CH gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CRx(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CRx(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRx gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CRx(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRx gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CRy(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CRy(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRy gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CRy(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRy gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CRz(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CRz(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRz gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CRz(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CRz gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CS(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CS(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CS gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CS(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CS gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CSWAP(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CSWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control: int, target_0: int, target_1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSWAP gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CSWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSWAP gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CSX(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CSX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CSX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CSXdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CSXdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSXdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CSXdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSXdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CSdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CSdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CSdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CSdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CU1(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CU1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CU1 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CU1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CU1 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CU3(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CU3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CU3 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CU3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CU3 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CV(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CV(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CV gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CV(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CV gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CVdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CVdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CVdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CVdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CVdg gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CX(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CX gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CY(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CY(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CY gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CY(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CY gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- CZ(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
CZ(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: int, target_qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CZ gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
CZ(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, control_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, target_qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a CZ gate on the wires for the specified control and target qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ECR(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ECR(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit_0: int, qubit_1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ECR gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ECR(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ECR gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ESWAP(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ESWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ESWAP gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ESWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ESWAP gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- FSim(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
FSim(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an FSim gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
FSim(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an FSim gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- GPI(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
GPI(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a GPI gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
GPI(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a GPI gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- GPI2(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
GPI2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a GPI2 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
GPI2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a GPI2 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- H(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
H(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Hadamard gate.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
H(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Hadamard gate.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ISWAP(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ISWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ISWAP gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ISWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ISWAP gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ISWAPMax(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ISWAPMax(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ISWAPMax gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ISWAPMax(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an ISWAPMax gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Measure(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Measure(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, bit_index: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single-qubit measurement in the computational (Z) basis.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Measure(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, bit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single-qubit measurement in the computational (Z) basis.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Phase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: Union[sympy.Expr, float], **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
- PhasedISWAP(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
PhasedISWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a PhasedISWAP gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
PhasedISWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a PhasedISWAP gate with posisbly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- PhasedX(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
PhasedX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a PhasedX gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
PhasedX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a PhasedX gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Reset(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Reset(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Reset operation. Sets a qubit to the Z-basis 0 state. Non-unitary operation.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Reset(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Reset operation. Sets a qubit to the Z-basis 0 state. Non-unitary operation.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Rx(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Rx(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Rx gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Rx(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Rx gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Ry(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Ry(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Ry gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Ry(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Ry gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Rz(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Rz(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Rz gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Rz(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an Rz gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- S(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
S(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an S gate (equivalent to U1(0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
S(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an S gate (equivalent to Rz(0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- SWAP(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
SWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit_0: int, qubit_1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SWAP gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
SWAP(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SWAP gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- SX(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
SX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SX gate (equivalent to Rx(0.5,-) up to a 0.25 global phase).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
SX(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SX gate (equivalent to Rx(0.5,-) up to a 0.25 global phase).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- SXdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
SXdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SXdg gate (equivalent to Rx(-0.5,-) up to a -0.25 global phase).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
SXdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a SXdg gate (equivalent to Rx(-0.5,-) up to a -0.25 global phase).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Sdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Sdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an S-dagger gate (equivalent to U1(-0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Sdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an S-dagger gate (equivalent to Rz(-0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Sycamore(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Sycamore(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Sycamore gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Sycamore(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Sycamore gate on the wires for the specified qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- T(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
T(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a T gate (equivalent to U1(0.25,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
T(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a T gate (equivalent to Rz(0.25,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- TK1(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
TK1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a TK1 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
TK1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a TK1 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- TK2(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
TK2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a TK2 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
TK2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a TK2 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Tdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Tdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a T-dagger gate (equivalent to U1(-0.25,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Tdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a T-dagger gate (equivalent to Rz(-0.25,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- U1(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
U1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U1 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
U1(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U1 gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- U2(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
U2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U2 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
U2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U2 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- U3(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
U3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U3 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
U3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle1: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], angle2: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a U3 gate with possibly symbolic angles (specified in half-turns).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- V(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
V(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a V gate (equivalent to Rx(0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
V(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a V gate (equivalent to Rx(0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Vdg(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Vdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a V-dagger gate (equivalent to Rx(-0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Vdg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a V-dagger gate (equivalent to Rx(-0.5,-)).
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- X(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
X(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
X(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an X gate.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- XXPhase(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
XXPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a XX gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
XXPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, angle: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a XX gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- XXPhase3(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
XXPhase3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, qubit2: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a 3-qubit XX gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified three qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
XXPhase3(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit2: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a 3-qubit XX gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified three qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Y(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Y(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Y(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Y gate.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- YYPhase(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
YYPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a YY gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
YYPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, angle: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a YY gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- Z(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
Z(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
Z(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a Z gate.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ZZMax(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ZZMax(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a ZZMax gate on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ZZMax(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a ZZMax gate on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- ZZPhase(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
ZZPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: int, qubit1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a ZZ gate with a possibly symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
ZZPhase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], qubit0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a ZZ gate with a symbolic angle (specified in half-turns) on the wires for the specified two qubits.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Overloaded function.
__init__(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) -> None
Constructs a circuit with a completely empty DAG.
__init__(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, name: str) -> None
Constructs a named circuit with a completely empty DAG.
- Parameters:
name – name for the circuit
__init__(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, n_qubits: int, name: Optional[str] = None) -> None
Constructs a circuit with a given number of qubits/blank wires.
>>> c = Circuit() >>> c.add_blank_wires(3)
is equivalent to
>>> c = Circuit(3)
- Parameters:
n_qubits – The number of qubits in the circuit
name – Optional name for the circuit.
__init__(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, n_qubits: int, n_bits: int, name: Optional[str] = None) -> None
Constructs a circuit with a given number of quantum and classical bits
- Parameters:
n_qubits – The number of qubits in the circuit
n_bits – The number of classical bits in the circuit
name – Optional name for the circuit.
- add_assertion(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_assertion(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ProjectorAssertionBox, qubits: Sequence[int], ancilla: Optional[int] = None, name: Optional[str] = None) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ProjectorAssertionBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – ProjectorAssertionBox to append
qubits – indices of target qubits
ancilla – index of ancilla qubit
name – name used to identify this assertion
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_assertion(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ProjectorAssertionBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], ancilla: Optional[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit] = None, name: Optional[str] = None) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ProjectorAssertionBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – ProjectorAssertionBox to append
qubits – target qubits
ancilla – ancilla qubit
name – name used to identify this assertion
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_assertion(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.StabiliserAssertionBox, qubits: Sequence[int], ancilla: int, name: Optional[str] = None) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
StabiliserAssertionBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – StabiliserAssertionBox to append
qubits – indices of target qubits
ancilla – index of ancilla qubit
name – name used to identify this assertion
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_assertion(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.StabiliserAssertionBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], ancilla: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, name: Optional[str] = None) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
StabiliserAssertionBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – StabiliserAssertionBox to append
qubits – target qubits
ancilla – ancilla qubit
name – name used to identify this assertion
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_barrier(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_barrier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubits: Sequence[int], bits: Sequence[int] = [], data: str = ‘’) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a Barrier on the given units
- Parameters:
data – additional data stored in the barrier
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_barrier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, units: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], data: str = ‘’) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a Barrier on the given units
- Parameters:
data – additional data stored in the barrier
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_blank_wires(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, number: int) None¶
Adds a number of new qubits to the circuit. These will be added to the default register (‘q’) if possible, filling out the unused indices from 0.
- Parameters:
number – Number of qubits to add
- add_c_and(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_and(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: int, arg1_in: int, arg_out: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a binary AND operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
arg0_in – first input bit
arg1_in – second input bit
arg_out – output bit
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_and(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_and().
- add_c_and_to_registers(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, reg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Applies bitwise AND to linear registers.
The operation is applied to the bits with indices 0, 1, 2, … in each register, up to the size of the smallest register.
- Parameters:
reg0_in – first input register
reg1_in – second input register
reg_out – output register
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_c_copybits(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_copybits(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, args_in: Sequence[int], args_out: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a classical copy operation
- Parameters:
args_in – source bits
args_out – destination bits
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_copybits(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, args_in: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], args_out: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_copybits().
- add_c_copyreg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, input_reg: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, output_reg: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Copy a classical register to another. Copying is truncated to the size of the smaller of the two registers.
- add_c_modifier(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_modifier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args_in: Sequence[int], arg_inout: int, name: str = ‘ExplicitModifier’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
- Parameters:
name – operation name
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_modifier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args_in: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], arg_inout: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, name: str = ‘ExplicitModifier’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_modifier().
- add_c_not(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_not(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg_in: int, arg_out: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a NOT operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
arg_in – input bit
arg_out – output bit
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_not(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_not().
- add_c_not_to_registers(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, reg_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Applies bitwise NOT to linear registers.
The operation is applied to the bits with indices 0, 1, 2, … in each register, up to the size of the smallest register.
- Parameters:
reg_in – input register
reg_out – name of output register
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_c_or(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_or(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: int, arg1_in: int, arg_out: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a binary OR operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
arg0_in – first input bit
arg1_in – second input bit
arg_out – output bit
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_or(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_or().
- add_c_or_to_registers(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, reg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Applies bitwise OR to linear registers.
The operation is applied to the bits with indices 0, 1, 2, … in each register, up to the size of the smallest register.
- Parameters:
reg0_in – first input register
reg1_in – second input register
reg_out – output register
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_c_predicate(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_predicate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args_in: Sequence[int], arg_out: int, name: str = ‘ExplicitPredicate’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
- Parameters:
name – operation name
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_predicate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args_in: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, name: str = ‘ExplicitPredicate’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_predicate().
- add_c_range_predicate(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_range_predicate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, minval: int, maxval: int, args_in: Sequence[int], arg_out: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a range-predicate operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
minval – lower bound of input in little-endian encoding
maxval – upper bound of input in little-endian encoding
args_in – input bits
arg_out – output bit (distinct from input bits)
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_range_predicate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, minval: int, maxval: int, args_in: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a range-predicate operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
minval – lower bound of input in little-endian encoding
maxval – upper bound of input in little-endian encoding
args_in – input bits
arg_out – output bit (distinct from input bits)
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_c_register(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, name: str, size: int) -> pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister
Constructs a new classical register with a given name and number of bits.
- Parameters:
name – Unique readable name for the register
size – Number of bits required
- Returns:
a map from index to the corresponding UnitIDs
add_c_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, register: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister) -> pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister
Adds BitRegister to Circuit
- Parameters:
register – BitRegister
- add_c_setbits(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_setbits(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends an operation to set some bit values.
- Parameters:
values – values to set
args – bits to set
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_setbits(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[bool], args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_setbits().
- add_c_setreg(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, value: int, arg: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Set a classical register to an unsigned integer value. The little-endian bitwise representation of the integer is truncated to the register size, up to _TKET_REG_WIDTH bit width. It is zero-padded if the width of the register is greater than _TKET_REG_WIDTH.
- add_c_transform(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_transform(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[int], args: Sequence[int], name: str = ‘ClassicalTransform’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a purely classical transformation, defined by a table of values, to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
values – table of values: bit \(j\) (in little-endian order) of the term indexed by \(sum_i a_i 2^i\) is output \(j\) of the transform applied to inputs \((a_i)\).
args – bits to which the transform is applied
name – operation name
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_transform(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, values: Sequence[int], args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], name: str = ‘ClassicalTransform’, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_transform().
- add_c_xor(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_c_xor(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: int, arg1_in: int, arg_out: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a binary XOR operation to the end of the circuit.
- Parameters:
arg0_in – first input bit
arg1_in – second input bit
arg_out – output bit
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_c_xor(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, arg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
See
add_c_xor().
- add_c_xor_to_registers(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, reg0_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg1_in: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, reg_out: pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister, **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Applies bitwise XOR to linear registers.
The operation is applied to the bits with indices 0, 1, 2, … in each register, up to the size of the smallest register.
- Parameters:
reg0_in – first input register
reg1_in – second input register
reg_out – output register
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_circbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_circbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circbox: pytket._tket.circuit.CircBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
CircBoxto the circuit.The qubits and bits of the
CircBoxare wired into the circuit in lexicographic order. Bits follow qubits in the order of arguments.- Parameters:
circbox – The box to append
args – Indices of the (default-register) qubits/bits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_circbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circbox: pytket._tket.circuit.CircBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
CircBoxto the circuit.The qubits and bits of the
CircBoxare wired into the circuit in lexicographic order. Bits follow qubits in the order of arguments.- Parameters:
circbox – The box to append
args – The qubits/bits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_circbox_regwise(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circbox: pytket._tket.circuit.CircBox, qregs: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister], cregs: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister], **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Append a
CircBoxto the circuit, wiring whole registers together.- Parameters:
circbox – The box to append
qregs – Sequence of
QubitRegisterfrom the outerCircuit, the order corresponding to the lexicographic order of corresponding registers in theCircBoxcregs – Sequence of
BitRegisterfrom the outerCircuit, the order corresponding to the lexicographic order of corresponding registers in theCircBox
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_circbox_with_regmap(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circbox: pytket._tket.circuit.CircBox, qregmap: dict[str, str], cregmap: dict[str, str], **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Append a
CircBoxto the circuit, wiring whole registers together.This method expects two maps (one for qubit registers and one for bit registers), which must have keys corresponding to all register names in the box. The box may not contain any qubits or bits that do not belong to a register, i.e. all must be single-indexed contiguously from zero.
- Parameters:
circbox – The box to append
qregmap – Map specifying which qubit register in the
CircBox(the map’s keys) matches which register in the outer circuit (the map’s values)cregmap – Map specifying which bit register in the
CircBox(the map’s keys) matches which register in the outer circuit (the map’s values)
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_circuit(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_circuit(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circuit: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], bits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit] = []) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
In-place sequential composition of circuits, appending a copy of the argument onto the end of the circuit. Connects qubits and bits with the same behaviour as
add_gate().- Parameters:
circuit – The circuit to be appended to the end of self
qubits – List mapping the (default register) qubits of circuit to the qubits of self
bits – List mapping the (default register) bits of circuit to the bits of self
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_circuit(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circuit: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qubits: Sequence[int], bits: Sequence[int] = []) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
In-place sequential composition of circuits, appending a copy of the argument onto the end of the circuit. Connects qubits and bits with the same behaviour as
add_gate().- Parameters:
circuit – The circuit to be appended to the end of self
qubits – List mapping the (default register) qubits of circuit to the (default register) qubits of self
bits – List mapping the (default register) bits of circuit to the (default register) bits of self
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_classicalexpbox_bit(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, expression: pytket.circuit.logic_exp.BitLogicExp, target: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Append a
ClassicalExpBoxover Bit to the circuit.- Parameters:
classicalexpbox – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_classicalexpbox_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, expression: pytket.circuit.logic_exp.RegLogicExp, target: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], **kwargs) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Append a
ClassicalExpBoxover BitRegister to the circuit.- Parameters:
classicalexpbox – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_conditional_barrier(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_conditional_barrier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, barrier_qubits: Sequence[int], barrier_bits: Sequence[int], condition_bits: Sequence[int], value: int, data: str = ‘’) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a Conditional Barrier on the given barrier qubits and barrier bits, conditioned on the given condition bits.
- Parameters:
barrier_qubits – Qubit in Barrier operation.
barrier_bits – Bit in Barrier operation.
condition_bits – Bit covering classical control condition of barrier operation.
value – Value that classical condition must have to hold (little-endian).
data – Additional data stored in Barrier operation.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_conditional_barrier(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, barrier_args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], condition_bits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], value: int, data: str = ‘’) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a Conditional Barrier on the given barrier qubits and barrier bits, conditioned on the given condition bits.
- Parameters:
barrier_args – Qubit and Bit in Barrier operation.
condition_bits – Bit covering classical control condition of barrier operation.
value – Value that classical condition must have to hold (little-endian).
data – Additional data stored in Barrier operation.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_conjugation_box(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_conjugation_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ConjugationBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ConjugationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_conjugation_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ConjugationBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ConjugationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_custom_gate(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_custom_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, definition: pytket._tket.circuit.CustomGateDef, params: Sequence[typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float]], qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append an instance of a
CustomGateDefto the circuit.- Parameters:
def – The custom gate definition
params – List of parameters to instantiate the gate with, in halfturns
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_custom_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, definition: pytket._tket.circuit.CustomGateDef, params: Sequence[typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float]], qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append an instance of a
CustomGateDefto the circuit.- Parameters:
def – The custom gate definition
params – List of parameters to instantiate the gate with, in halfturns
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_diagonal_box(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_diagonal_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.DiagonalBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
DiagonalBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_diagonal_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.DiagonalBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
DiagonalBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_dummybox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_dummybox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, dummybox: pytket._tket.circuit.DummyBox, qubits: Sequence[int], bits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
DummyBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
dummybox – The box to append
qubits – Indices (in the default register) of the qubits to append the box to
bits – Indices of the bits (in the default register) to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_dummybox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, dummybox: pytket._tket.circuit.DummyBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], bits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Bit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
DummyBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
dummybox – The box to append
qubits – Qubits to append the box to
bits – Bits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_expbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_expbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, expbox: pytket._tket.circuit.ExpBox, qubit_0: int, qubit_1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append an
ExpBoxto the circuit.The matrix representation is ILO-BE.
- Parameters:
expbox – The box to append
qubit_0 – Index of the first target qubit
qubit_1 – Index of the second target qubit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_expbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, expbox: pytket._tket.circuit.ExpBox, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append an
ExpBoxto the circuit.The matrix representation is ILO-BE.
- Parameters:
expbox – The box to append
qubit_0 – The first target qubit
qubit_1 – The second target qubit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_gate(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, Op: pytket._tket.circuit.Op, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single operation to the end of the circuit on some particular qubits/bits. The number of qubits/bits specified must match the arity of the gate.
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, Op: pytket._tket.circuit.Op, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single operation to the end of the circuit on some particular qubits/bits. The number of qubits/bits specified must match the arity of the gate.
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single (non-parameterised) gate to the end of the circuit on some particular qubits from the default register (‘q’). The number of qubits specified must match the arity of the gate. For OpType.Measure operations the bit from the default register should follow the qubit.
>>> c.add_gate(OpType.H, [0]) # equivalent to c.H(0) >>> c.add_gate(OpType.CX, [0,1]) # equivalent to c.CX(0,1)
- Parameters:
type – The type of operation to add
args – The list of indices for the qubits/bits to which the operation is applied
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single (non-parameterised) gate to the end of the circuit on some particular qubits from the default register (‘q’). The number of qubits specified must match the arity of the gate. For OpType.Measure operations the bit from the default register should follow the qubit.
>>> c.add_gate(OpType.H, [0]) # equivalent to c.H(0) >>> c.add_gate(OpType.CX, [0,1]) # equivalent to c.CX(0,1)
- Parameters:
type – The type of operation to add
args – The qubits/bits to apply the gate to
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single gate, parameterised by an expression, to the end of circuit on some particular qubits from the default register (‘q’).
- Parameters:
type – The type of gate to add
angle – The parameter for the gate in halfturns
args – The list of indices for the qubits to which the operation is applied
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, angle: typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float], args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single gate, parameterised by an expression, to the end of circuit on some particular qubits from the default register (‘q’).
- Parameters:
type – The type of gate to add
angle – The parameter for the gate in halfturns
args – The qubits/bits to apply the gate to
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, angles: Sequence[typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float]], args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single gate, parameterised with a vector of expressions corresponding to halfturns, to the end of circuit on some particular qubits from the default register (‘q’).
- Parameters:
type – The type of gate to add
angles – The parameters for the gate in halfturns
args – The list of indices for the qubits to which the operation is applied
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_gate(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType, angles: Sequence[typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float]], args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Appends a single gate to the end of the circuit
- Parameters:
type – The type of gate to add
params – The parameters for the gate in halfturns
args – The qubits/bits to apply the gate to
kwargs – Additional properties for classical conditions
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_multiplexed_tensored_u2(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_multiplexed_tensored_u2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedTensoredU2Box, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedTensoredU2Boxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_multiplexed_tensored_u2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedTensoredU2Box, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedTensoredU2Boxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_multiplexedrotation(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_multiplexedrotation(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedRotationBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedRotationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_multiplexedrotation(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedRotationBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedRotationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_multiplexedu2(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_multiplexedu2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedU2Box, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedU2Boxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_multiplexedu2(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexedU2Box, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexedU2Boxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_multiplexor(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_multiplexor(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexorBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexorBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_multiplexor(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.MultiplexorBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
MultiplexorBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_pauliexpbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_pauliexpbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexpbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexpbox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_pauliexpbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexpbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexpbox – The box to append
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_pauliexpcommutingsetbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_pauliexpcommutingsetbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexpcommutingsetbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpCommutingSetBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpCommutingSetBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexpcommutingsetbox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_pauliexpcommutingsetbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexpcommutingsetbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpCommutingSetBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpCommutingSetBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexpcommutingsetbox – The box to append
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_pauliexppairbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_pauliexppairbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexppairbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpPairBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpPairBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexppairbox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_pauliexppairbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, pauliexppairbox: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpPairBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PauliExpPairBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
pauliexppairbox – The box to append
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_phase(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, a: Union[sympy.Expr, float]) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Add a global phase to the circuit.
- Parameters:
a – Phase to add, in halfturns
- Returns:
circuit with added phase
- add_phasepolybox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_phasepolybox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, phasepolybox: pytket._tket.circuit.PhasePolyBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PhasePolyBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
phasepolybox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_phasepolybox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, phasepolybox: pytket._tket.circuit.PhasePolyBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
PhasePolyBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
phasepolybox – The box to append
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_q_register(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_q_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, name: str, size: int) -> pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister
Constructs a new quantum register with a given name and number of qubits.
- Parameters:
name – Unique readable name for the register
size – Number of qubits required
- Returns:
a map from index to the corresponding UnitIDs
add_q_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, register: pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister) -> pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister
Adds QubitRegister to Circuit
- Parameters:
register – QubitRegister
- add_qcontrolbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_qcontrolbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qcontrolbox: pytket._tket.circuit.QControlBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
QControlBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
qcontrolbox – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_qcontrolbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, qcontrolbox: pytket._tket.circuit.QControlBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
QControlBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
qcontrolbox – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_qubit(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, id: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, reject_dups: bool = True) None¶
Constructs a single qubit with the given id.
- Parameters:
id – Unique id for the qubit
reject_dups – Fail if there is already a qubit in this circuit with the id. Default to True
- add_state_preparation_box(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_state_preparation_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.StatePreparationBox, args: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
StatePreparationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_state_preparation_box(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.StatePreparationBox, args: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
StatePreparationBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
box – The box to append
args – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_termsequencebox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_termsequencebox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, termsequencebox: pytket._tket.circuit.TermSequenceBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
TermSequenceBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
termsequencebox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_termsequencebox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, termsequencebox: pytket._tket.circuit.TermSequenceBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
TermSequenceBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
termsequencebox – The box to append
qubits – The qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_toffolibox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_toffolibox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, toffolibox: pytket._tket.circuit.ToffoliBox, qubits: Sequence[int], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ToffoliBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
toffolibox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_toffolibox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, toffolibox: pytket._tket.circuit.ToffoliBox, qubits: Sequence[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit], **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
ToffoliBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
toffolibox – The box to append
qubits – Indices of the qubits to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_unitary1qbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_unitary1qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary1qBox, qubit_0: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary1qBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
unitarybox – The box to append
qubit_0 – Index of the qubit to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_unitary1qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary1qBox, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary1qBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
unitarybox – The box to append
qubit_0 – The qubit to append the box to
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_unitary2qbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_unitary2qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary2qBox, qubit_0: int, qubit_1: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary2qBoxto the circuit.The matrix representation is ILO-BE.
- Parameters:
unitarybox – The box to append
qubit_0 – Index of the first target qubit
qubit_1 – Index of the second target qubit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_unitary2qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary2qBox, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary2qBoxto the circuit.The matrix representation is ILO-BE.
- Parameters:
unitarybox – The box to append
qubit_0 – The first target qubit
qubit_1 – The second target qubit
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_unitary3qbox(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
add_unitary3qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary3qBox, qubit_0: int, qubit_1: int, qubit_2: int, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary3qBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
unitarybox – box to append
qubit_0 – index of target qubit 0
qubit_1 – index of target qubit 1
qubit_2 – index of target qubit 2
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
add_unitary3qbox(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, unitarybox: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary3qBox, qubit_0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_1: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, qubit_2: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, **kwargs) -> pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit
Append a
Unitary3qBoxto the circuit.- Parameters:
unitarybox – box to append
qubit_0 – index of target qubit 0
qubit_1 – index of target qubit 1
qubit_2 – index of target qubit 2
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_wasm(funcname: str, filehandler: WasmFileHandler, list_i: Sequence[int], list_o: Sequence[int], args: Sequence[int] | Sequence[Bit], args_wasm: Sequence[int] | None = None, **kwargs: Any) Circuit¶
Add a classical function call from a wasm file to the circuit.
- Parameters:
funcname – name of the function that is called
filehandler – wasm file handler to identify the wasm file
list_i – list of the number of bits in the input variables
list_o – list of the number of bits in the output variables
args – vector of circuit bits the wasm op should be added to
args_wasm – vector of wasmstates the wasm op should be added to
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- add_wasm_to_reg(funcname: str, filehandler: WasmFileHandler, list_i: Sequence[BitRegister], list_o: Sequence[BitRegister], args_wasm: Sequence[int] | None = None, **kwargs: Any) Circuit¶
Add a classical function call from a wasm file to the circuit.
- Parameters:
funcname – name of the function that is called
filehandler – wasm file handler to identify the wasm file
list_i – list of the classical registers assigned to the input variables of the function call
list_o – list of the classical registers assigned to the output variables of the function call
args_wasm – vector of wasmstates the wasm op should be added to
kwargs – additional arguments passed to add_gate_method . Allowed parameters are opgroup, condition , condition_bits, condition_value
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- append(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, circuit: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) None¶
In-place sequential composition of circuits, appending a copy of the argument onto the end of the circuit. Inputs and Outputs are unified if they share the same id, defaulting to parallel composition if there is no match.
- Parameters:
circuit – The circuit to be appended to the end of self
- property bit_readout¶
A map from bit to its (left-to-right) index in readouts from backends (following the increasing lexicographic order convention)
- property bits¶
A list of all classical bit ids in the circuit
- property c_registers¶
Get all classical registers.
The list only includes registers that are singly-indexed contiguously from zero.
- Returns:
List of
BitRegister
- commands_of_type(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, optype: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType) list[pytket._tket.circuit.Command]¶
Get all commands in a circuit of a given type.
The order is consistent with the causal order of the operations in the circuit.
- Parameters:
optype – operation type
- Returns:
list of
Command
- copy(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
- Returns:
an identical copy of the circuit
- property created_qubits¶
A list of qubits whose input is a Create operation
- dagger(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Given a pure circuit (i.e. without any measurements or conditional gates), produces a new circuit for the inverse/adjoint operation.
- Returns:
a new
Circuitcorresponding to the inverse operation
- depth(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) int¶
Returns the number of interior vertices on the longest path through the DAG, excluding vertices representing barrier operations.
>>> c = Circuit(3) >>> c.depth() 0 >>> c.CX(0,1) >>> c.CX(1,2) >>> c.CX(2,0) >>> c.depth() 3
- Returns:
the circuit depth
- depth_2q(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) int¶
Returns the number of vertices in the longest path through the sub-DAG consisting of vertices with 2 quantum wires,excluding vertices representing barrier operations.
>>> c = Circuit(3) >>> c.CZ(0,1) >>> c.Z(0) >>> c.Z(1) >>> c.ZZMax(1,2) >>> c.CX(1,2) >>> c.depth_2q() 3 :return: the circuit depth with respect to 2-qubit operations.
- depth_by_type(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
depth_by_type(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType) -> int
Returns the number of vertices in the longest path through the sub-DAG consisting of vertices representing operations of the given type.
>>> c = Circuit(3) >>> c.CX(0,1) >>> c.Z(1) >>> c.CX(1,2) >>> c.depth_by_type(OpType.CX) 2
- Parameters:
type – the operation type of interest
- Returns:
the circuit depth with respect to operations matching type
depth_by_type(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, types: set[pytket._tket.circuit.OpType]) -> int
Returns the number of vertices in the longest path through the sub-DAG consisting of vertices representing operations of the given types.
>>> c = Circuit(3) >>> c.CZ(0,1) >>> c.Z(1) >>> c.CX(1,2) >>> c.depth_by_type({OpType.CZ, OpType.CX}) 2
- Parameters:
types – the set of operation types of interest
- Returns:
the circuit depth with respect to operations matching an element of types
- property discarded_qubits¶
A list of qubits whose output is a Discard operation
- flatten_registers(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) dict[pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID, pytket._tket.unit_id.UnitID]¶
Combines all qubits into a single register namespace with the default name, and likewise for bits
- free_symbols(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) set[sympy.Symbol]¶
- Returns:
set of symbolic parameters in the circuit
- static from_dict(arg0: dict) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Construct Circuit instance from JSON serializable dictionary representation of the Circuit.
- get_c_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, name: str) pytket._tket.unit_id.BitRegister¶
Get the classical register with the given name.
- Parameters:
name – name for the register
- Returns:
the retrieved
BitRegister
- get_commands(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) list[pytket._tket.circuit.Command]¶
- Returns:
a list of all the Commands in the circuit
- get_counts(*others: Circuit, backend=None, **params) list[ndarray][source]¶
Runs a circuit on a backend and returns the counts.
- get_q_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, name: str) pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister¶
Get the quantum register with the given name.
- Parameters:
name – name for the register
- Returns:
the retrieved
QubitRegister
- get_resources(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) pytket._tket.circuit.ResourceData¶
Calculate the overall resources of the circuit.
This takes account of the data stored in each py:class:DummyBox within the circuit, as well as other gates, to compute upper and lower bounds.
- Returns:
bounds on resources of the circuit
>>> resource_data0 = ResourceData( ... op_type_count={ ... OpType.T: ResourceBounds(1, 2), ... OpType.H: ResourceBounds(0, 1), ... OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(1, 2), ... OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(3, 3), ... }, ... gate_depth=ResourceBounds(5, 8), ... op_type_depth={ ... OpType.T: ResourceBounds(0, 10), ... OpType.H: ResourceBounds(0, 10), ... OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(1, 2), ... OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(3, 3), ... }, ... two_qubit_gate_depth=ResourceBounds(4, 5), ... ) >>> dbox0 = DummyBox(n_qubits=2, n_bits=0, resource_data=resource_data0) >>> resource_data1 = ResourceData( ... op_type_count={ ... OpType.T: ResourceBounds(2, 2), ... OpType.H: ResourceBounds(1, 1), ... OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(2, 3), ... OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(3, 5), ... }, ... gate_depth=ResourceBounds(5, 10), ... op_type_depth={ ... OpType.T: ResourceBounds(1, 2), ... OpType.H: ResourceBounds(2, 4), ... OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(1, 1), ... OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(3, 4), ... }, ... two_qubit_gate_depth=ResourceBounds(3, 5), ... ) >>> dbox1 = DummyBox(n_qubits=3, n_bits=0, resource_data=resource_data1) >>> c = ( ... Circuit(3) ... .H(0) ... .CX(1, 2) ... .CX(0, 1) ... .T(2) ... .H(1) ... .add_dummybox(dbox0, [0, 1], []) ... .CZ(1, 2) ... .add_dummybox(dbox1, [0, 1, 2], []) ... .H(2) ... ) >>> resource_data = c.get_resources() >>> print(resource_data) ResourceData(op_type_count={OpType.T: ResourceBounds(4, 5), OpType.H: ResourceBounds(4, 5), OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(5, 7), OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(7, 9), }, gate_depth=ResourceBounds(15, 23), op_type_depth={OpType.T: ResourceBounds(2, 12), OpType.H: ResourceBounds(5, 17), OpType.CX: ResourceBounds(4, 5), OpType.CZ: ResourceBounds(7, 8), }, two_qubit_gate_depth=ResourceBounds(10, 13))
- get_statevector(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) numpy.ndarray[numpy.complex128[m, 1]]¶
Calculate the unitary matrix of the circuit, using ILO-BE convention, applied to the column vector (1,0,0…), which is thus another column vector. Due to pybind11 and numpy peculiarities, to treat the result as a genuine column vector and perform further matrix multiplication, you need to call .reshape(rows,1) to get a 2D matrix with the correct dimensions.
- Returns:
The calculated vector.
- get_unitary(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) numpy.ndarray[numpy.complex128[m, n]]¶
- Returns:
The numerical unitary matrix of the circuit, using ILO-BE convention.
- get_unitary_times_other(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, matr: numpy.ndarray[numpy.complex128[m, n]]) numpy.ndarray[numpy.complex128[m, n]]¶
Calculate UM, where U is the numerical unitary matrix of the circuit, with ILO-BE convention, and M is another matrix. This is more efficient than calculating U separately, if M has fewer columns than U.
- Parameters:
matr – The matrix to be multiplied.
- Returns:
The product of the circuit unitary and the given matrix.
- implicit_qubit_permutation(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) dict[pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit, pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit]¶
- Returns:
dictionary mapping input qubit to output qubit on the same path
- property is_simple¶
Checks that the circuit has only 1 quantum and 1 classic register using the default names (‘q’ and ‘c’). This means it is suitable to refer to qubits simply by their integer indices.
- is_symbolic(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) bool¶
- Returns:
True if the circuit contains any free symbols, False otherwise.
- measure_all(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Appends a measure gate to all qubits, storing the results in the default classical register. Bits are added to the circuit if they do not already exist.
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- measure_register(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: pytket._tket.unit_id.QubitRegister, arg1: str) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Appends a measure gate to all qubits in the given register, storing the results in the given classical register with matching indices.The classical register will be created if it doesn’t exist.
- Parameters:
qreg – the QubitRegister to be measured
creg_name – the name of the BitRegister to store the results
- Returns:
the new
Circuit
- n_1qb_gates(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) int¶
Returns the number of vertices in the dag with one quantum edge.Ignores Input, Create, Output, Discard, Reset, Measure and Barrier vertices.
- n_2qb_gates(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) int¶
Returns the number of vertices in the dag with two quantum edges.Ignores Input, Create, Output, Discard, Reset, Measure and Barrier vertices.
- property n_bits: int¶
Number of bits in a circuit.
- property n_gates¶
- Returns:
the number of gates in the Circuit
- n_gates_of_type(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, type: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType) int¶
Returns the number of vertices in the dag of a given operation type.
>>> c.CX(0,1) >>> c.H(0) >>> c.CX(0,1) >>> c.n_gates_of_type(OpType.CX) 2
- Parameters:
type – The operation type to search for
- Returns:
the number of operations matching type
- n_nqb_gates(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, size: int) int¶
Returns the number of vertices in the dag with given number of quantum edges.Ignores Input, Create, Output, Discard, Reset, Measure and Barrier vertices.
- property n_qubits¶
- Returns:
the number of qubits in the circuit
- property name¶
- property opgroups¶
A set of all opgroup names in the circuit
- ops_of_type(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, optype: pytket._tket.circuit.OpType) list[pytket._tket.circuit.Op]¶
Get all operations in the circuit of a given type.
The order is not guaranteed.
- Parameters:
optype – operation type
- Returns:
list of
Op
- property phase¶
- Returns:
the global phase applied to the circuit, in halfturns (not meaningful for circuits with classical interactions)
- property q_registers¶
Get all quantum registers.
The list only includes registers that are singly-indexed contiguously from zero.
- Returns:
List of
QubitRegister
- qubit_create(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit) None¶
Make a quantum input a Create operation (initialized to 0
- qubit_create_all(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) None¶
Make all quantum inputs Create operations (initialized to 0)
- qubit_discard(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit) None¶
Make a quantum output a Discard operation
- qubit_discard_all(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) None¶
Make all quantum outputs Discard operations
- qubit_is_created(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit) bool¶
Query whether a qubit has its initial state set to zero
- qubit_is_discarded(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arg0: pytket._tket.unit_id.Qubit) bool¶
Query whether a qubit has its final state discarded
- property qubit_readout¶
A map from qubit to its (left-to-right) index in readouts from backends. A qubit will feature in this map if it is measured and neither it nor the bit containing the measurement result is subsequently acted on
- property qubit_to_bit_map¶
A map from qubit to the bit it is measured to. A qubit will feature in this map if it is measured and neither it nor the bit containing the measurement result is subsequently acted on
- property qubits¶
A list of all qubit ids in the circuit
- remove_blank_wires(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, keep_blank_classical_wires: bool = False) None¶
Removes any Input-Output pairs in the DAG with no intervening operations, i.e. removes untouched qubits/bits from the circuit. This may occur when optimisations recognise that the operations on a qubit reduce to the identity, or when routing adds wires to “fill out” the architecture. This operation will only remove empty classical wires if there are no used bits with a higher index in the same register.
- Parameters:
keep_blank_classical_wires – select if empty classical wires should not be removed
- replace_SWAPs(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) None¶
Replace all SWAP gates with implicit wire swaps.
- replace_implicit_wire_swaps(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) None¶
Replace all implicit wire swaps with SWAP gates.
- substitute_named(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, op: pytket._tket.circuit.Op, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given op.The replacement operations retain the same name.
- Parameters:
op – the replacement operation
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, repl: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given circuit.Named operations in the replacement circuit must not match any named operations in the circuit being modified.
- Parameters:
repl – the replacement circuit
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.CircBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement CircBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary1qBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement Unitary1qBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary2qBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement Unitary2qBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.Unitary3qBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement Unitary3qBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ExpBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement ExpBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.PauliExpBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement PauliExpBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.ToffoliBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement ToffoliBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.DummyBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement DummyBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.QControlBox, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement QControlBox
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
substitute_named(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, box: pytket._tket.circuit.CustomGate, opgroup: str) -> bool
Substitute all ops with the given name for the given box.The replacement boxes retain the same name.
- Parameters:
box – the replacement CustomGate
opgroup – the name of the operations group to replace
- Returns:
whether any replacements were made
- symbol_substitution(*args, **kwargs)¶
Overloaded function.
symbol_substitution(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, symbol_map: dict[sympy.Symbol, typing.Union[sympy.Expr, float]]) -> None
In-place substitution for symbolic expressions; iterates through each parameterised gate/box and performs the substitution.
- Parameters:
symbol_map – A map from SymPy symbols to SymPy expressions
symbol_substitution(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, symbol_map: dict[sympy.Symbol, float]) -> None
In-place substitution for symbolic expressions; iterates through each gate/box and performs the substitution.
- Parameters:
symbol_map – A map from SymPy symbols to floating-point values
- to_dict(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) dict¶
- Returns:
a JSON serializable dictionary representation of the Circuit
- to_latex_file(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, filename: str) None¶
Produces a latex file with a visualisation of the circuit using the Quantikz package.
- Parameters:
filename – Name of file to write output to (must end in “.tex”)
- transpose(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit) pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit¶
Given a pure circuit (i.e. without any measurements or conditional gates), produces a new circuit for the transpose operation.
- Returns:
a new
Circuitcorresponding to the transpose operation
- valid_connectivity(self: pytket._tket.circuit.Circuit, arch: pytket._tket.architecture.Architecture, directed: bool, allow_bridge: bool = False) bool¶
Confirms whether all two qubit gates in given circuit are along some edge of the architecture.
- Parameters:
arch – The architecture capturing the desired connectivity
directed – If true, also checks that CX or ECR gates are in the same direction as the edges of the architecture
allow_bridge – Accept BRIDGEs as valid, assuming the middle qubit neighbours the others
- Returns:
True or False
lambeq.backend.pennylane¶
PennyLane interface¶
Lambeq’s interface with Pennylane circuits. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause ‘New’ or ‘Revised’ License.
Notes¶
If probabilities is set to False, the output states of the PennyLane circuit will be exactly equivalent to those of the lambeq circuit (for the same parameters).
If probabilities is set to True, the output states of the PennyLane
circuit will be the probabilities of the output states, equivalent
to appending lambeq.backend.quantum.Measure to all the
open wires in the lambeq circuit.
Once a PennyLaneCircuit has been constructed, it
can be evaluated with eval(). If the circuit contains only
concrete parameters (i.e. no symbolic parameters), no arguments
should be passed to eval(). If the circuit contains symbolic
parameters, a list of the symbolic parameters and a list of their
associated weights should be passed to eval() as symbols= and
weights=.
- class lambeq.backend.pennylane.PennyLaneCircuit(ops, symbols, params, wires, probabilities, post_selection, scale, n_qubits, backend_config, diff_method)[source]¶
Bases:
objectImplement a pennylane circuit with post-selection.
- __init__(ops, symbols, params, wires, probabilities, post_selection, scale, n_qubits, backend_config, diff_method)[source]¶
- contains_sympy()[source]¶
Determine if the circuit parameters are concrete or contain SymPy symbols.
- Returns:
- bool
Whether the circuit parameters contain SymPy symbols.
- draw()[source]¶
Print a string representation of the circuit similar to qml.draw, but including post-selection.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of
sympy.core.symbol.Symbol, default: None The symbols from the original lambeq circuit.
- weightslist of
torch.FloatTensor, default: None The weights to substitute for the symbols.
- symbolslist of
- eval()[source]¶
Evaluate the circuit. The symbols should be those from the original lambeq diagram, which will be substituted for the concrete parameters in weights.
- Parameters:
- symbolslist of
sympy.core.symbol.Symbol, default: None The symbols from the original lambeq circuit.
- weightslist of
torch.FloatTensor, default: None The weights to substitute for the symbols.
- symbolslist of
- Returns:
torch.TensorThe post-selected output of the circuit.
- get_device(backend_config)[source]¶
Return a PennyLane device with the specified backend configuration.
- get_valid_states()[source]¶
Determine which of the output states of the circuit are compatible with the post-selections.
- Returns:
- list of int
The indices of the circuit output that are compatible with the post-selections.
- initialise_concrete_params(symbol_weight_map)[source]¶
Given concrete values for each of the SymPy symbols, substitute the symbols for the values to obtain concrete parameters, via the param_substitution method.
- initialise_device_and_circuit()[source]¶
Initialise the PennyLane device and circuit when instantiating the PennyLaneCirucit, or loading from disk.
- make_circuit()[source]¶
Construct the
qml.Qnode, a circuit that can be used with autograd to construct hybrid models.- Returns:
qml.QnodeA Pennylane circuit without post-selection.
- lambeq.backend.pennylane.extract_ops_from_tk(tk_circ)[source]¶
Extract the operations, and corresponding parameters and wires, from a pytket Circuit. Return these as lists to use in constructing PennyLane circuit.
- Parameters:
- tk_circ
lambeq.backend.converters.tk.Circuit The pytket circuit to extract the operations from.
- tk_circ
- Returns:
- list of
qml.operation.Operation The PennyLane operations extracted from the pytket circuit.
- list of list of (
torch.FloatTensoror sympy.core.symbol.Symbol)The corresponding parameters of the operations.
- list of list of int
The corresponding wires of the operations.
- set of
sympy.core.symbol.Symbol The free symbols in the parameters of the tket circuit.
- list of
- lambeq.backend.pennylane.get_post_selection_dict(tk_circ)[source]¶
Return post-selections based on qubit indices.
- Parameters:
- tk_circ
lambeq.backend.converters.tk.Circuit The pytket circuit to extract the post-selections from.
- tk_circ
- Returns:
- dict of int
A mapping from qubit indices to pytket classical indices.
- lambeq.backend.pennylane.tk_op_to_pennylane(tk_op)[source]¶
Extract the operation, parameters and wires from a pytket
Op, and return the corresponding PennyLane operation.- Parameters:
- tk_op
pytket.circuit.Op The pytket
Opto convert.
- tk_op
- Returns:
qml.operation.OperationThe PennyLane operation equivalent to the input pytket Op.
- list of (
torch.FloatTensoror sympy.core.symbol.Symbol)The parameters of the operation.
- list of
sympy.core.symbol.Symbol The free symbols in the parameters of the operation.
- list of int
The wires/qubits to apply the operation to.
- lambeq.backend.pennylane.to_pennylane(lambeq_circuit: Diagram, probabilities=False, backend_config=None, diff_method='best')[source]¶
Return a PennyLaneCircuit equivalent to the input lambeq circuit. probabilities determines whether the PennyLaneCircuit returns states (as in lambeq), or probabilities (to be more compatible with automatic differentiation in PennyLane).
- Parameters:
- lambeq_circuit
lambeq.backend.quantum.Diagram The lambeq circuit to convert to PennyLane.
- probabilitiesbool, default: False
Determines whether the PennyLane circuit outputs states or un-normalized probabilities. Probabilities can be used with more PennyLane backpropagation methods.
- backend_configdict, default: None
A dictionary of PennyLane backend configration options, including the provider (e.g. IBM or Honeywell), the device, the number of shots, etc. See the PennyLane plugin documentation for more details.
- diff_methodstr, default: “best”
The differentiation method to use to obtain gradients for the PennyLane circuit. Some gradient methods are only compatible with simulated circuits. See the PennyLane documentation for more details.
- lambeq_circuit
- Returns:
PennyLaneCircuitThe PennyLane circuit equivalent to the input lambeq circuit.
lambeq.backend.drawing¶
lambeq’s drawing module.
- class lambeq.backend.drawing.DrawableDiagram(boxes: list[~lambeq.backend.drawing.drawable.BoxNode] = <factory>, wire_endpoints: list[~lambeq.backend.drawing.drawable.WireEndpoint] = <factory>, wires: list[tuple[int, int]] = <factory>)[source]¶
Bases:
objectRepresentation of a lambeq diagram carrying all information necessary to render it.
- Attributes:
- boxes: list of BoxNode
Boxes in the diagram.
- wire_endpoints: list of WireEndpoint
Endpoints for all wires in the diagram.
- wires: list of tuple of the form (int, int)
The wires in a diagram, each represented by the indices of its 2 endpoints in wire_endpoints.
- __init__(boxes: list[~lambeq.backend.drawing.drawable.BoxNode] = <factory>, wire_endpoints: list[~lambeq.backend.drawing.drawable.WireEndpoint] = <factory>, wires: list[tuple[int, int]] = <factory>) None¶
- boxes: list[BoxNode]¶
- classmethod from_diagram(diagram: Diagram, foliated: bool = False) Self[source]¶
Builds a graph representation of the diagram, calculating coordinates for each box and wire.
- Parameters:
- diagramgrammar Diagram
A lambeq diagram.
- foliatedbool, default: False
If true, each box of the diagram is drawn in a separate layer. By default boxes are compressed upwards into available space.
- Returns:
- drawableDrawableDiagram
Representation of diagram including all coordinates necessary to draw it.
- scale_and_pad(scale: tuple[float, float], pad: tuple[float, float])[source]¶
Scales and pads the diagram as specified.
- Parameters:
- scaletuple of 2 floats
Scaling factors for x and y axes respectively.
- padtuple of 2 floats
Padding values for x and y axes respectively.
- wire_endpoints: list[WireEndpoint]¶
- wires: list[tuple[int, int]]¶
- lambeq.backend.drawing.draw(diagram: Diagram, **params) None[source]¶
Draw a grammar diagram.
- Parameters:
- diagram: Diagram
Diagram to draw.
- draw_as_nodesbool, optional
Whether to draw boxes as nodes, default is False.
- colorstring, optional
Color of the box or node, default is white (‘#ffffff’) for boxes and red (‘#ff0000’) for nodes.
- textpadpair of floats, optional
Padding between text and wires, default is (0.1, 0.1).
- draw_type_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw type labels, default is True.
- draw_box_labelsbool, optional
Whether to draw box labels, default is True.
- aspectstring, optional
Aspect ratio, one of [‘auto’, ‘equal’].
- marginstuple, optional
Margins, default is (0.05, 0.05).
- nodesizefloat, optional
BoxNode size for spiders and controlled gates.
- fontsizeint, optional
Font size for the boxes, default is 12.
- fontsize_typesint, optional
Font size for the types, default is 12.
- figsizetuple, optional
Figure size.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- to_tikzbool, optional
Whether to output tikz code instead of matplotlib.
- asymmetryfloat, optional
Make a box and its dagger mirror images, default is .25 * any(box.is_dagger for box in diagram.boxes).
- foliatedbool, default: False
If true, each box of the diagram is drawn in a separate layer. By default boxes are compressed upwards into available space.
- lambeq.backend.drawing.draw_equation(*terms: Diagram, symbol: str = '=', space: float = 1, path: str | None = None, **params) None[source]¶
Draw an equation with multiple diagrams.
- Parameters:
- terms: list of Diagrams
Diagrams in equation.
- symbol: str
Symbol separating equations. ‘=’ by default.
- space: float
Amount of space between adjacent diagrams.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- **params:
Additional drawing parameters, passed to
draw().
- lambeq.backend.drawing.draw_pregroup(diagram: Diagram, **params) None[source]¶
Draw a pregroup grammar diagram.
- A pregroup diagram is structured as:
(State @ State … State) >> (Cups and Swaps)
- Parameters:
- diagram: Diagram
Diagram to draw.
- draw_as_nodesbool, optional
Whether to draw boxes as nodes, default is False.
- colorstring, optional
Color of the box or node, default is white (‘#ffffff’) for boxes and red (‘#ff0000’) for nodes.
- textpadpair of floats, optional
Padding between text and wires, default is (0.1, 0.1).
- aspectstring, optional
Aspect ratio, one of [‘auto’, ‘equal’].
- marginstuple, optional
Margins, default is (0.05, 0.05).
- fontsizeint, optional
Font size for the boxes, default is 12.
- fontsize_typesint, optional
Font size for the types, default is 12.
- figsizetuple, optional
Figure size.
- pathstr, optional
Where to save the image, if None we call plt.show().
- to_tikzbool, optional
Whether to output tikz code instead of matplotlib.
- lambeq.backend.drawing.render_as_str(diagram: Diagram, word_spacing: int = 2, use_at_separator: bool = False, compress_layers: bool = True, use_ascii: bool = False) str[source]¶
Render a grammar diagram as text.
Presently only implemented for pregroup diagrams.
- Parameters:
- diagram: Diagram
Diagram to draw.
- word_spacingint, default: 2
The number of spaces between the words of the diagrams.
- use_at_separatorbool, default: False
Whether to represent types using @ as the monoidal product. Otherwise, use the unicode dot character.
- compress_layersbool, default: True
Whether to draw boxes in the same layer when they can occur simultaneously, otherwise, draw one box per layer.
- use_ascii: bool, default: False
Whether to draw using ASCII characters only, for compatibility reasons.
- Returns:
- str
Drawing of diagram in string format.
- lambeq.backend.drawing.to_gif(diagrams: list[Diagram], path: str | None = None, timestep: int = 500, loop: bool = False, **params) str | HTML_ty[source]¶
Build a GIF stepping through the given diagrams.
- Parameters:
- diagrams: list of Diagrams
Sequence of diagrams to draw.
- pathstr
Where to save the image, if None a gif gets created.
- timestepint, optional
Time step in milliseconds, default is 500.
- loopbool, optional
Whether to loop, default is False
- paramsany, optional
Passed to Diagram.draw.
- Returns:
- IPython.display.HTML or str
HTML to display the generated GIF
lambeq.backend.snake_removal¶
Snake removal¶
This module contains a function for removing snakes from diagrams. This work is based on DisCoPy (https://discopy.org/) which is released under the BSD 3-Clause “New” or “Revised” License.
- exception lambeq.backend.snake_removal.InterchangerError(box0: Box, box1: Box)[source]¶
Bases:
ExceptionThis is raised when we try to interchange conected boxes.
- add_note()¶
Exception.add_note(note) – add a note to the exception
- args¶
- with_traceback()¶
Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
- lambeq.backend.snake_removal.interchange(diagram: Diagram, i: int, j: int, left: bool = False) Diagram[source]¶
Returns a new diagram with boxes i and j interchanged.
Gets called recursively whenever
i < j + 1 or j < i - 1.- Parameters:
- diagram
Diagram The diagram to interchange boxes in.
- iint
Index of the box to interchange.
- jint
Index of the new position for the box.
- leftbool, optional
Whether to apply left interchangers.
- diagram
Notes
By default, we apply only right exchange moves:
top >> Id(left @ box1.dom @ mid) @ box0 @ Id(right) >> Id(left) @ box1 @ Id(mid @ box0.cod @ right) >> bottom
gets rewritten to:
top >> Id(left) @ box1 @ Id(mid @ box0.dom @ right) >> Id(left @ box1.cod @ mid) @ box0 @ Id(right) >> bottom
- lambeq.backend.snake_removal.normalize(diagram: Diagram, left: bool = False) Iterator[Diagram][source]¶
Implements normalization of diagrams, see arXiv:1804.07832.
- Parameters:
- diagram
Diagram The diagram to normalize.
- leftbool, optional
Passed to
interchange().
- diagram
- Yields:
- diagram
Diagram Rewrite steps.
- diagram
Examples
>>> from lambeq.backend.grammar import Ty, Box >>> s0, s1 = Box('s0', Ty(), Ty()), Box('s1', Ty(), Ty()) >>> gen = normalize(s0 @ s1) >>> for _ in range(3): print(next(gen)) |Ty() @ [s1; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [s0; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()| |Ty() @ [s0; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [s1; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()| |Ty() @ [s1; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [s0; Ty() -> Ty()] @ Ty()|
- lambeq.backend.snake_removal.snake_removal(diagram: Diagram, left: bool = False) Iterator[Diagram][source]¶
Returns a generator which yields normalization steps.
- Parameters:
- leftbool, optional
Whether to apply left interchangers.
- Yields:
- diagram
Diagram Rewrite steps.
- diagram
Examples
>>> from lambeq.backend.grammar import Ty, Box, Cup, Cap, Id >>> n, s = Ty('n'), Ty('s') >>> cup, cap = Cup(n, n.r), Cap(n.r, n) >>> f = Box('f', n, n) >>> g = Box('g', s @ n, n) >>> h = Box('h', n, n @ s) >>> diagram = g @ cap >> f.dagger() @ Id(n.r) @ f >> cup @ h >>> for d in snake_removal(diagram): ... print(d) |Ty... >> |Ty() @ [CUP; Ty(n) @ Ty(n).r -> Ty()] @ Ty(n)| >>... |Ty... >> |Ty(n) @ [CAP; Ty() -> Ty(n).r @ Ty(n)] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [CUP; Ty(n) @ Ty(n).r -> Ty()] @ Ty(n)| >>... |Ty() @ [g; Ty(s) @ Ty(n) -> Ty(n)] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [f†; Ty(n) -> Ty(n)] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [f; Ty(n) -> Ty(n)] @ Ty()| >> |Ty() @ [h; Ty(n) -> Ty(n) @ Ty(s)] @ Ty()|